What is Industrial Labeling?
Industrial labeling is crucial in today's world due to its role in ensuring operational efficiency, safety, regulatory compliance, as well as track and traceability. As supply chains are becoming increasingly complex and global, precise labeling enables the seamless tracking and management of products from manufacturing through distribution to the end-user. Labels provide essential information such as product identification, compliance certifications, batch numbers, and expiration dates, which are vital for object identification, vehicle identification, inventory control, quality assurance, and recall management. In industries where safety and regulatory adherence are extremely important, such as pharmaceuticals, chemicals, automotive, and food and beverage, industrial labeling is crucial for preventing accidents and ensuring that products meet legal standards.
Industrial labeling refers to the practice of creating and applying labels to products, equipment, and various assets within an industrial setting. The primary purpose of industrial labeling is to ensure that items can be easily identified, tracked, and managed throughout their lifecycle, from production to disposal. This process involves the use of durable materials and printing methods to ensure that the labels withstand harsh industrial environments, including exposure to chemicals, extreme temperatures, and physical abrasion. Industrial labels must also be securely applied to a wide variety of objects that have different shapes, sizes, and surface types.
As part of Industry 4.0, the rise of automated systems and the Internet of Things (IoT) has further increased the importance of industrial labeling. Printers that are manually operated are now becoming connected and controlled by smarter systems and cloud-based labeling solutions.
There are two main types of technologies used for industrial labeling and identification. Radio-based technologies like Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) and optical character recognition systems that include 1D and 2D codes like barcodes and data matrix codes (DMC), or Quick Response (QR) codes. Integrating these technologies into labeling systems enables real-time tracking and data collection. The result: Increased transparency and operational efficiency. This capability is crucial for optimizing digitalization in logistics, reducing errors, and supporting data-driven decision-making processes.
Another technology that is used for industrial labeling is Near-Field Communication (NFC), a sub category of RFID. NFC technology is used in applications that require interactions in a close proximity. In addition to consumer engagement, product identification, and inventory control, NFC labels enable applications such as temperature monitoring to counterfeit protection.
RFID vs. Optical Codes
How do companies choose which industrial labeling technology to use? In order to make this decision, it is necessary to know the differences between RFID and optical character recognition technologies. Companies need to know what they want to track, how secure the information needs to be, how and where inventory tracking will take place, and consider the overall budget.
RFID systems use radio waves to communicate between a tag and a reader. RFID tags and labels contain a microchip and an antenna This enables the storage of higher volumes of data, compared to barcodes. One of the key advantages of RFID is its ability to be read from a distance without requiring a direct line of sight. This capability, coupled with the potential to read multiple tags simultaneously, makes RFID highly efficient for bulk reading and tracking applications. Additionally, RFID tags are durable, capable of withstanding harsh environmental conditions, and can incorporate security features like encryption and password protection, which improve data security.
In contrast, optical character recognition technologies, such as barcodes, QR codes, and data matrix codes, rely on visual scanning. Barcodes are the most traditional form, consisting of parallel lines representing data that a scanner reads. While barcodes are quick and efficient for individual item scanning, they require a direct line of sight and can store only a limited amount of information, typically up to 20-25 characters. Barcodes are widely used in retail for product identification, point-of-sale transactions, and basic inventory management. However, they can be easily damaged by scratches, dirt, or moisture, making them less durable compared to RFID.
2D codes like QR codes and data matrix codes are more advanced forms of optical labeling. QR codes consist of black squares arranged on a white background and can store up to 4,296 alphanumeric characters. They can be scanned using cameras on smartphones or specialized readers and are used for various applications such as marketing, product labeling, and event ticketing. Data matrix codes, on the other hand, offer even higher data density and can store up to 2,335 alphanumeric characters in a small space. They are particularly useful in industries where space is limited, such as electronics manufacturing, medical devices, and aerospace, where they can be marked directly on materials to ensure durability in harsh environments. This process is called direct part marking (DPM).
Wireless IoT Technologies and Industrial Labeling
Industrial Labeling Systems and Labeling Software
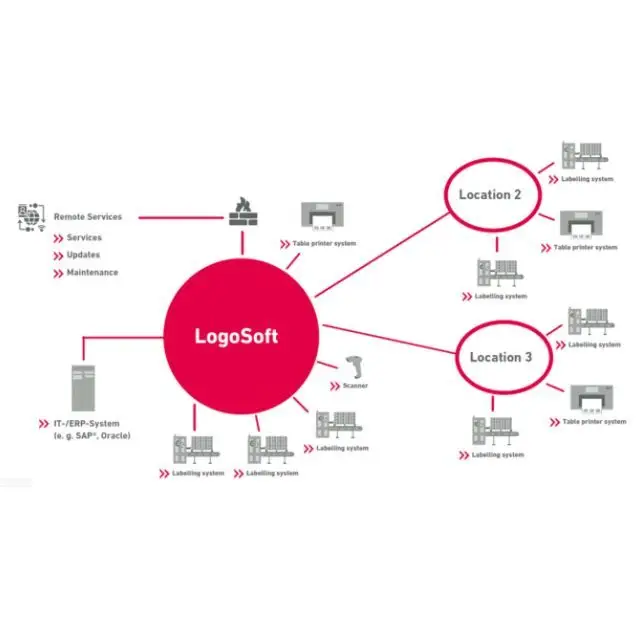
The production and application of industrial labels is achieved by using industrial labeling systems. Industrial labeling systems refer to the hardware and software used for the production and application of physical labels, or to directly mark products. There are many types of industrial labeling systems:
Print and Apply Labeling Systems
These systems automatically print labels and apply them to products, packages, or pallets. They are widely used in high-volume production environments to ensure consistent and accurate labeling. Key components of this system are label printers that are capable of printing barcode labels, QR codes, text and graphics, as well as applicators.
Direct Part Marking (DPM) Systems
DPM systems involve directly marking products with identification information without using separate labels. These systems are crucial for permanent identification and traceability. Methods include: Laser marking, dot preen marking, and inkjet marking.
Thermal Transfer Labeling Systems
Thermal transfer printers use heat to transfer ink from a ribbon onto a label material. This method is known for its durability and is used for printing barcodes, text, and graphics that need to withstand harsh environments. Stand-alone printers are incorporated into production lines for continuous labeling.
RFID Labeling Systems
These systems involve printing and encoding RFID tags and labels. RFID labels store more information than barcodes and can be read without a direct line of sight, making them ideal for advanced tracking and inventory management. RFID printers are used to print and encode information on the RFID tags and labels while RFID applicators are used to apply them to products or packaging.
NFC Labeling Systems
NFC labeling systems include standalone NFC label printers, NFC tags or labels, and fixed or handheld NFC readers. NFC-enabled smartphones can also be used to read the tags and labels.
Automated Label Applicators
Automated applicators are used to apply pre-printed labels to products. They can be integrated into production lines and are designed for high-speed, precise application. Tamp-blow applicators and wipe-on applicators are typically used for this.
Handheld Labeling Systems
Handheld labelers are portable devices used for on-the-spot labeling in various industrial settings, such as warehouses, construction sites, and maintenance operations. These include handheld thermal printers and label dispensers.
Heat Shrink Labeling Systems
These systems are used primarily for labeling cables and wires. The labels are made from heat-shrinkable materials that, when heated, shrink to fit securely around the item being labeled. Part of these systems are heat shrink printers and heat guns.
Labeling Software
In addition to all these different types of industrial labeling systems, labeling software is used for designing, managing, and controlling the label printing process. Label design software enables users to create custom label designs with text, barcodes, graphics, and more. Label software programs also enable users to generate QR codes and barcodes automatically. This is done by entering a Uniform Resource Locator (URL) or European Article Number (EAN) code in the interface.
Label design software is also important to monitor regulatory compliance. This is achieved through the management of serialization and traceability that is required by industrial regulations, such as the GS1 Digital Link, Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Lablling of Chemicals (GHS), Unique Device Identifier (UDI), FDA 21 CFR Part 11/GMP Annex 11, EU Food Information to Consumers (FIC), and the ATA SPEC 2000.
RFID tags also have their own set of certifications that they must adhere to, including International Standards Organization (ISO), GS1, and Electronic Product Code (EPC), for example. Different certifications are required for different industries.
Vision Systems
Vision systems are also used to verify the accuracy and placement of labels. They use cameras and software to inspect labels for correctness, ensuring compliance and reducing errors. These systems contain barcode verifiers and label inspection systems.
Facts & Figures
According to a report by the research and consulting firm “Verified Market Research”, the global market for industrial labels will grow by 5.18 percent between 2024 and 2030. Drivers of this growth include the increased demand for regulatory compliance and counterfeit protection measures, growing industrialization, and the development in labeling technologies. According to the market research platform “Gitnux”, the manufacturing industry had a 33 percent market share of the global market for industrial labels. In 2020, the automotive industry had a market share of 25 percent.
Successful Examples of IoT-Based Industrial Labeling
RFID technology is increasingly being used for industrial labeling and identification in many industries. The following real-world examples show how RFID is used for identification in production, the automotive industry, and for the film industry.
Window Identification at Toro Aluminium

Toro Aluminium, a Canadian window and door supplier for high-rise buildings, has used UHF RFID to identify prefabricated aluminum components since 2023. Aluminum profiles are cut to size via CNC machines. RFID printers integrated into the CNC machines generate coded RFID labels containing production details like dimensions. These are connected to the ERP system and are captured by RFID ceiling antennas from Feig Electronic on the assembly lines, and by RFID antennas from Times-7 at the area of outgoing goods.
Toro Aluminium, a Canadian window and door supplier for high-rise buildings, has used UHF RFID to identify prefabricated aluminum components since 2023. Aluminum profiles are cut to size via CNC machines. RFID printers integrated into the CNC machines generate coded RFID labels containing production details like dimensions. These are connected to the ERP system and are captured by RFID ceiling antennas from Feig Electronic on the assembly lines, and by RFID antennas from Times-7 at the area of outgoing goods.

“We implemented the pilot project in their facility for six months on one entry point of the production line, and on one shipping door. We gave them pre-printed and pre-encoded labels that were manually applied. The purpose of this was to compare the results coming from this, compared to the previous barcode system. The results were very motiviating and it showed them the potential in the technology. They saw the difference between automated scans with the RFID and the manual scans by operators of the previous barcode system.”

Khaled Elshimy
CEO
Vehicle Identification at Audi
Since 2020, every all-electric e-tron GT vehicle at Audi’s Neckarsulm production site has been fitted with a UHF RFID transponder that is affixed to the car body panel. Each car body is thereby assigned a unique identity, containing data such as model, paintwork, and motorization. RFID readers capture this data, which is then accessible via a centralized IT system. Throughout production, vehicles are identified at predetermined checkpoints.
"We meet the quality requirement of 99.8 percent reading accuracy in all production plants. The RFID tag ensures digital real-time access to all relevant vehicle data from production. This includes the body shape, paintwork, motorization and features of each vehicle. Vehicle identification takes place across the board in all production processes. This means that we can guarantee that the vehicle ordered is manufactured and subsequently delivered exactly according to the customer's wishes at any point in time."
Identification of Rented Items at Rentex
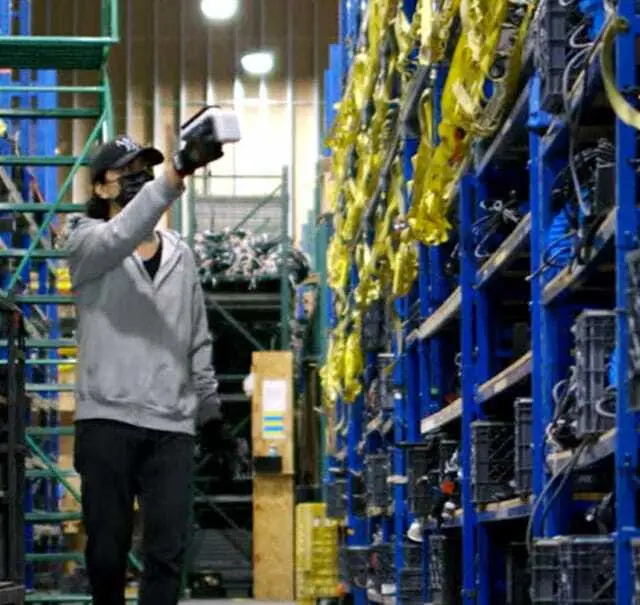

US film equipment supplier Rentex has introduced a UHF RFID solution from HID to facilitate the identification of rental items. Over 200,000 items have been fitted with passive RFID tags. Employees use a handheld RFID reader to track and identify the items. The tagged items can be read at a distance of up to 10 meters. Items can be read in large quantities within a few seconds without visual contact. This corresponds to a time saving of 99.24 percent. This makes the identification process more efficient.
US film equipment supplier Rentex has introduced a UHF RFID solution from HID to facilitate the identification of rental items. Over 200,000 items have been fitted with passive RFID tags. Employees use a handheld RFID reader to track and identify the items. The tagged items can be read at a distance of up to 10 meters. Items can be read in large quantities within a few seconds without visual contact. This corresponds to a time saving of 99.24 percent. This makes the identification process more efficient.

"Imagine going into the cable section of a warehouse. There are 25,000 cables on various shelves and you’ve got to locate and pull a unique cable that’s there. What these companies are finding is that by using RFID, they hugely shortcut all of these processes so that identifying where something is on a shelf is now very easy. You can walk into the cable section and turn on your handheld RFID reader. You can turn on a functionality called the Geiger Counter where the reader pings faster as you get closer to the object you’re seeking. It guides you to the particular cable."

Richard Aufreiter
VP Product Marketing
More Stories on Industrial Labeling
The Future of Industrial Labeling and Identification Technologies
The future of industrial labeling and identification technologies is marked by a strong emphasis on sustainability and the integration of advanced technologies.
Smart labels are becoming increasing used for industrial product labeling and industrial marking. An example of this is the world’s first printable 5G smart labels for logistics shipment tracking that was introduced by the company Reelables at the end of 2023. This development goes a step further and eliminates the need for the manual scanning and reading of RFID or barcode labels. As augmented reality (AR) technologies become more widely accessible, AR labels are likely to grow in demand. Companies like Buffalo Red Wings, Lego, Red Bull, and 19 Crimes already use AR labels. These labels will provide users with a more dynamic way of engaging with digital content. Another future trend is the integration of IoT with AR labels that could lead to AR experiences that are more context-aware.
New technology standards like the GS1 Digital Link will also contribute to transforming the industrial labeling industry. GS1 Digital Link enables the embedding of web links within barcodes, QR codes, and NFC tags, allowing consumers and businesses to access product information online. This standard aims to improve transparency, traceability, and user engagement. Initiatives like the Amazon Transparency Program use unique transparency codes to verify product authenticity and track items through the supply chain as a solution to counterfeiting and to ensure product integrity.
Sustainability for companies will continue to be a central focus in industrial labeling in the future. There will be a shift towards using eco-friendly materials and processes, such as biodegradable labels, recycling-compatible adhesives, and non-toxic inks. Companies will adopt sustainable practices to reduce their environmental footprint, driven by regulatory requirements and consumer demand for greener products. This will include designing labels that facilitate recycling and re-usability, contributing to a circular economy.
Advantages of Industrial Labeling and Identification
Advantages of Wireless IoT
- Improved transparency and visibility
- Enables counterfeit protection
- Improved inventory management
- Real-time tracking
- Increased safety and security
Industrial labeling and identification offer many advantages.
Effective industrial identification systems improve inventory control by providing real-time data on stock levels, locations, and movement. IoT-enabled labels enable the real-time tracking and monitoring of products and assets throughout the supply chain. This capability provides up-to-the-minute data on the location, status, and condition of items. This visibility helps companies optimize inventory levels, reduce excess stock, and prevent stockouts. Inventory management is improved and costs are saved.
Labels provide critical information that helps trace products throughout the supply chain. This traceability is essential for quality control, recall management, and verifying the authenticity of products. It ensures that companies can track the origin, movement, and history of their products with precision. Labels also contain safety information, such as hazard warnings, handling instructions, and emergency procedures to help protect workers and consumers. This information is crucial for preventing accidents, ensuring proper use of products and equipment, and maintaining a safe working environment.
IoT sensors embedded in labels or tags can be used for condition monitoring. The condition of assets and equipment can be monitored continuously in real-time, enabling predictive maintenance.
One of the key advantages of industrial labeling is to ensure compliance with industry regulations and standards. Many industries, such as automotive, pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, and chemicals, have strict labeling requirements to ensure safety and transparency. Proper labeling helps companies meet these legal obligations, avoiding fines and legal issues.
Industrial labeling and identification offer many advantages.
Effective industrial identification systems improve inventory control by providing real-time data on stock levels, locations, and movement. IoT-enabled labels enable the real-time tracking and monitoring of products and assets throughout the supply chain. This capability provides up-to-the-minute data on the location, status, and condition of items. This visibility helps companies optimize inventory levels, reduce excess stock, and prevent stockouts. Inventory management is improved and costs are saved.
Labels provide critical information that helps trace products throughout the supply chain. This traceability is essential for quality control, recall management, and verifying the authenticity of products. It ensures that companies can track the origin, movement, and history of their products with precision. Labels also contain safety information, such as hazard warnings, handling instructions, and emergency procedures to help protect workers and consumers. This information is crucial for preventing accidents, ensuring proper use of products and equipment, and maintaining a safe working environment.
IoT sensors embedded in labels or tags can be used for condition monitoring. The condition of assets and equipment can be monitored continuously in real-time, enabling predictive maintenance.
One of the key advantages of industrial labeling is to ensure compliance with industry regulations and standards. Many industries, such as automotive, pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, and chemicals, have strict labeling requirements to ensure safety and transparency. Proper labeling helps companies meet these legal obligations, avoiding fines and legal issues.
Advantages of Wireless IoT
- Improved transparency and visibility
- Enables counterfeit protection
- Improved inventory management
- Real-time tracking
- Increased safety and security
Challenges in Industrial Labeling and Identification
Although labels are used to ensure compliance with regulations and standards, these continue to evolve. Companies must keep up-to-date with the latest compliance regulations and practices that are introduced by governing bodies and industry associations.
It is extremely important for labels to be applied correctly to products in order to ensure that the correct information is made available to stakeholders across the supply chain. Errors in labeling can lead to product recalls and supply chain disruptions.
Companies that operate internationally must ensure that their product labels meet the respective language requirements, as well as any country-specific label regulations. Labeling software is used to develop labels in various languages.
It is also important to consider the environment surrounding labels. RFID labels for example are subject to interference in environments near metal or water. Barcodes are not suited for harsh environments that may damage the label and prevent proper reading and identification.
Partners Spezialized in Industrial Labeling Solutions
Outlook – Next-Level Industrial Labeling and Identification
Future trends in industrial labeling and identification are the increased integration of AI in labeling systems, AR labels for enhanced and dynamic customer engagement, and the increase in demand for personalized labels.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI has the potential to enhance labeling processes from the design of the label, to printing, and the labeling software. AI algorithms improve both the speed and accuracy of labeling processes. Labeling machines with AI are able to adapt to different product sizes and shapes.
Augmented Reality (AR) Labels
AR labels contain triggers or markers that is recognized by a respective AR app. By capturing the AR label with devices like smartphone or tablet cameras and AR glasses, the AR app or browser is able to identify the markers and trigger the digital content overlay. This includes the activation of videos, 3D models, animations, interactive games, for example.
Personalization
By leveraging advanced printing technologies, IoT integration, and data analytics, companies can create customized labels that improve traceability, compliance, efficiency, and customer satisfaction. The focus is on tailoring labels and identification markings to meet specific needs in order to increase customer satisfaction.
-über-Wi-Fi-HaLow-400.webp)