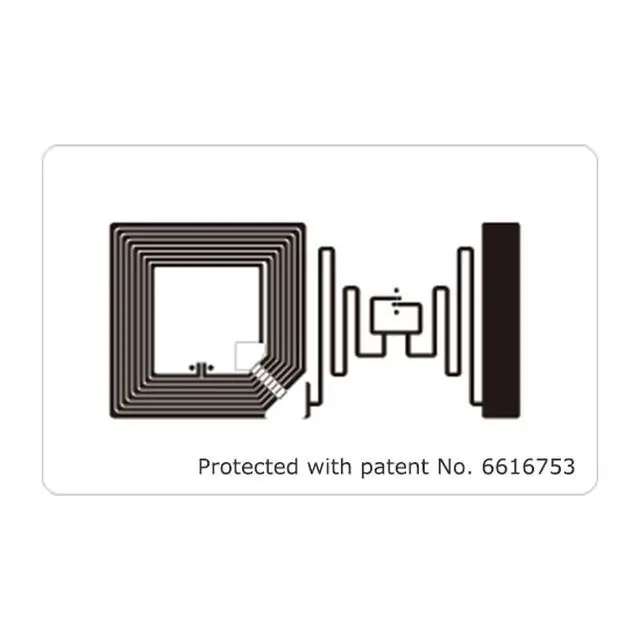
What is an NFC System?
NFC is the abbreviation for Near Field Communication. NFC technology is based on RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) and uses electromagnetic radio waves. NFC is therefore also a radio technology. NFC transmits on the frequency of 13.56 MHz. This frequency is also used by other RFID systems that operate in the high-frequency (HF) range. NFC is therefore an HF technology. NFC uses this frequency for wireless communication over short distances of typically just a few centimeters to enable fast and secure NFC data transmission.
How Are NFC Systems Structured?
At the heart of every NFC system is the NFC chip. This chip is either a transponder or reader chip and contains the NFC controller, which is responsible for processing the NFC communication protocols. It controls data transmission and reception via the NFC antenna. Each NFC device has integrated software components that control the hardware and enable the correct implementation of the NFC protocols.
The NFC antenna is mounted directly in or on an NFC-enabled device and enables the transmission and reception of electromagnetic radio waves. The antenna is tuned to the standardized frequency of 13.56 MHz for NFC communication.
An NFC tag has a simpler structure, consisting of an antenna and an NFC chip. Without its own power supply, the NFC tag is supplied with energy by the electromagnetic field of the NFC reader (in most cases a smartphone) as soon as it is in its vicinity.
How Does NFC Work?
Communication between NFC devices is based on bidirectional communication. When two NFC-enabled devices, or an NFC device and an NFC tag approach each other, the device with its own power supply (e.g. a smartphone) activates an electromagnetic field. This field induces a current in the passive device (e.g. an NFC tag), which supplies it with energy and starts to send data. Data is transmitted via the electromagnetic field using amplitude or frequency modulation. The information is then received and processed by the active device in the NFC capture range.
Developers use application programming interfaces (APIs) to gain access to NFC functionality. What is an NFC interface? These interfaces allow software developers to implement NFC-related functions such as reading tags, emulating a card, or wirelessly exchanging data between two devices in their applications.
Depending on the application, three different operating modes are used for NFC communication. The reader/writer mode, the peer-to-peer mode (P2P), and the card emulation mode. The P2P mode enables communication between two NFC-enabled devices. The two devices alternate and act as sender and receiver. A practical example is the exchange of files or contact data between two smartphones.
Operating Modes for Different Applications
One of the most important operating modes is the Card Emulation Mode. In this mode, an NFC-enabled device behaves like a contactless chip card. This is particularly useful for applications in the field of contactless payment and access control. For example, a smartphone can act as a digital wallet or electronic access card by holding it up to a reader. In this way, users can carry out secure transactions and gain access to secure areas without having to carry physical cards.
Another important operating mode of NFC is the read/write mode. In this mode, the NFC-enabled device acts as a reader that can read information from, and write to NFC tags or smart cards. This mode is often used in industrial applications to capture data from nameplates or warehouse labels quickly and efficiently. In logistics and retail, the read/write mode enables fast inventory and tracking of products. In marketing, interactive posters and information kiosks can be set up where the user holds their smartphone to an NFC tag to receive additional information or special offers.
The peer-to-peer mode is another operating mode that enables direct communication between two NFC-enabled devices. In this mode, the devices can exchange data by simply holding them together. This is particularly useful for quickly exchanging contact information, photos, or other files between smartphones. In an industrial environment, peer-to-peer mode can be used to synchronize machine configurations and maintenance data between devices and systems. This mode enables seamless and fast communication and data transfer between devices without the need for a central infrastructure.
Active or Passive? It Depends on the Application
In active mode, both NFC devices generate their own radio frequency field. This allows both devices to send and receive data. They communicate alternately as each device activates and deactivates its transmission. In passive mode, only one device generates an RF field, while the other device responds by using the energy of the electric field for communication.
Which Radio Technologies Can Be Combined with NFC Systems?
As already described, NFC is a form of HF RFID. NFC describes extended communication protocols or application-specific data formats that go beyond the HF RFID standards. By combining UHF RFID (see also next section) with NFC, e.g. in logistics processes, the extended possibilities of NFC can be utilized.
Bluetooth is often used to simplify pairing. Instead of navigating through multiple steps on a screen, two NFC-enabled devices can simply be held together to establish a Bluetooth connection. This is particularly useful for headphones, speakers, fitness trackers, and other wearable devices that require quick and easy pairing.
NFC can also be used to quickly transfer Wi-Fi settings such as SSID and password, allowing devices to connect to a Wi-Fi network without manual input. This is handy for smart home devices, printers, cameras, and other devices that need a simple and fast Wi-Fi connection.
Zigbee devices can be quickly added to a Zigbee network using NFC. This is particularly useful for smart home systems where Zigbee sensors and actuators can be integrated into the network through simple NFC interaction.
The biggest advantage of NFC-enabled devices is the simple and user-friendly way of networking devices and exchanging data. By simply touching two NFC-enabled devices, complex connection processes can be automated and simplified. In addition, NFC connections are relatively secure due to their very short range (a few centimetres), which minimizes the risk of unwanted eavesdropping attempts.
The biggest advantage of NFC-enabled devices is the simple and user-friendly way of networking devices and exchanging data. By simply touching two NFC-enabled devices, complex connection processes can be automated and simplified. In addition, NFC connections are relatively secure due to their very short range (a few centimetres), which minimizes the risk of unwanted eavesdropping attempts.
NFC Products
Facts & Figures
The market for NFC technology is growing as a result of a rising demand of NFC-enabled devices and services across different industries. According to the market data platform “World Metrics”, the global market for NFC technology will be valued at over 34 billion USD by 2027. From 2020, this would be a growth rate of 17.2 percent.
Within the market for NFC technology, the smartphone segment had the largest market share at 38 percent. In 2019, approximately five percent of all contactless card transactions worldwide were NFC transactions in the retail industry. Contactless payment methods with NFC have been used by approximately 18.2 percent of people in the world.
What Kind of NFC Solutions Are There?
NFC, or Near Field Communication, has established itself as an extremely successful technology in many areas. NFC is particularly widespread in the area of contactless payment. This technology allows users to carry out transactions quickly and securely by simply holding their smartphones or NFC-enabled cards up to a reader. This has revolutionized the way people shop and pay around the world, as it speeds up the payment process and reduces the need for physical cards or cash.
Another important area of application for NFC is access control. In many modern office buildings, hotels, and public facilities, NFC is used to control access to rooms or specific areas. Users can simply hold their NFC-enabled key fobs, cards, or smartphones up to a reader to open doors. This not only provides greater security, but also a more convenient way to grant and manage access.
NFC also plays a key role in wireless communication between devices. The technology is often used to simplify the pairing of Bluetooth devices. Instead of having to navigate through several steps on a screen, users can simply hold two NFC-enabled devices together to establish a Bluetooth connection. This is especially handy when using headphones, speakers, and other portable devices that require quick and easy pairing.
NFC is also becoming increasingly popular in the smart home sector. Here, the technology enables the simple integration and management of devices within a network. For example, Zigbee or Zigbee devices can be quickly added to a smart home network by simply holding them up to an NFC-enabled hub or gateway. This simplifies the installation process and enables seamless control and automation of the entire household.
Another innovative area of application for NFC can be found in advertising and marketing. By scanning NFC tags, consumers can receive additional information about products, unlock special offers, or take part in interactive advertising campaigns. This enables companies to interact with their customers in a creative way, improve the shopping experience, or communicate technical product information.
NFC is also used in the healthcare industry. Patients can use NFC-enabled wristbands or cards to quickly and securely confirm their identity, speeding up the check-in process in hospitals and clinics. NFC can also be used to pair medical devices and transfer data securely, increasing efficiency and accuracy in patient care.
NFC Solutions in Test Procedures
A typical area of application is the periodic inspection of operating equipment. In industry, machines and tools need to be checked regularly to ensure they are working properly and meet safety standards. With NFC, maintenance technicians can perform inspections more efficiently by simply holding an NFC-enabled device up to the machine for instant access to inspection logs, maintenance histories, and relevant data. This enables faster and more accurate equipment checks, reduces downtime, and improves the documentation of maintenance work. Equipment testing is also used for water meters or fire protection systems, for example.
Another important area of application is the parameterization of vending machines. Vending machines need to be regularly maintained and reconfigured to meet changing customer requirements. With NFC, technicians can simplify the parameterization of vending machines by simply holding an NFC-enabled device to the machine to quickly and accurately change settings such as price adjustments, product inventory, and promotions. This saves time and reduces the chance of errors compared to traditional manual input methods.
Reading nameplates is another typical NFC application scenario in industry. Nameplates contain important information about machines and components, such as serial numbers, manufacturing data and technical specifications. With NFC, this information can be read quickly and easily by holding an NFC-enabled device up to the nameplate. This is particularly useful in environments where quick identification and recording of machine data is required, such as in plant maintenance and repair. Automating the reading process increases efficiency and improves the accuracy of the captured data.
NFC Authentation at Collectors Universe
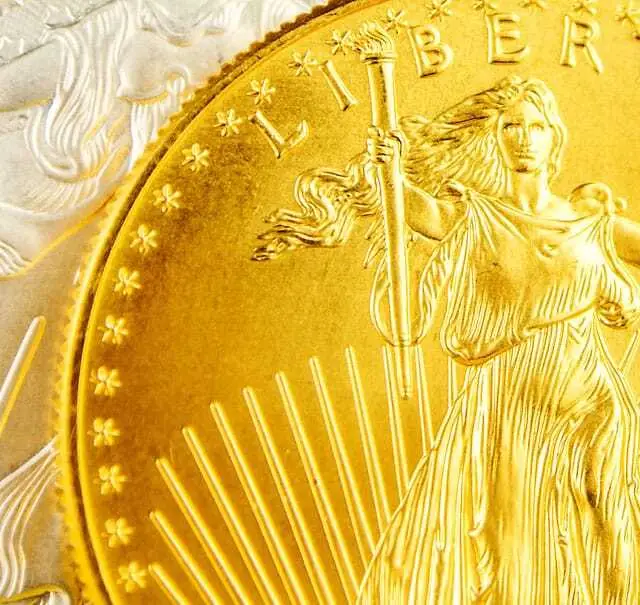

To enable customers to verify the authenticity of collector coins, the American company Collectors Universe uses NFC tags in combination with HID's Trsuted Tag Services. The NFC tags are attached to the packaging of collector coins underneath a PCGS label. By reading the NFC tags via an NFC-enabled smartphone, collectors can authenticate the coin via the Cloud Authentication Service platform. Now two million NFC tags are to be introduced for coins, medals, tokens and banknotes.
To enable customers to verify the authenticity of collector coins, the American company Collectors Universe uses NFC tags in combination with HID's Trsuted Tag Services. The NFC tags are attached to the packaging of collector coins underneath a PCGS label. By reading the NFC tags via an NFC-enabled smartphone, collectors can authenticate the coin via the Cloud Authentication Service platform. Now two million NFC tags are to be introduced for coins, medals, tokens and banknotes.

"The ultimate goal is to provide an authentication solution that is easy and convenient for the end user, and to provide a pleasant user experience. The verification processes run in the background, virtually automated – seamless to customer. All the user has to do is "tap" an NFC-enabled smartphone to the object. When a "tap" is made, either a green checkmark or a red "X" appears."

Mark Robinton
VP RTLS Business Unit
Contactless Payment with NFC by Cuploop

The Estonion start-up Cuploop has developed a reverse vending machine for the return of reusable packaging. These vending machines are placed at sports stadiums and concert halls, for example. Reusable cup or food containers that can be bought at these events are each equipped with an RFID chip. These can be returned via the reverse vending machine. By tapping a contactless card to the NFC bank terminal, a refund is calculated and money transferred back to the customer.
The Estonion start-up Cuploop has developed a reverse vending machine for the return of reusable packaging. These vending machines are placed at sports stadiums and concert halls, for example. Reusable cup or food containers that can be bought at these events are each equipped with an RFID chip. These can be returned via the reverse vending machine. By tapping a contactless card to the NFC bank terminal, a refund is calculated and money transferred back to the customer.

"The idea was to replace single-use with re-usable packaging. Our co-founder Marek attended an event in 2018 that tried to achieve this, but returning the packaging took a long time. The event organizers had problems with the existing systems that were not able to process refunds automatically. Refunding in cash or via app is too complicated at an event with 60,000 people. We started to figure out how to automate the collecting of re-usable packaging and the deposit refund, and to make this service as easy to use as possible. We don't ask anybody to download any kind of app, fill out a form or give us personal data. The only thing you need to use the solution is your bank card or smartphone."

Lauri Luik
CTO
Cold Chain - NFC Track & Trace in Use by TomKat
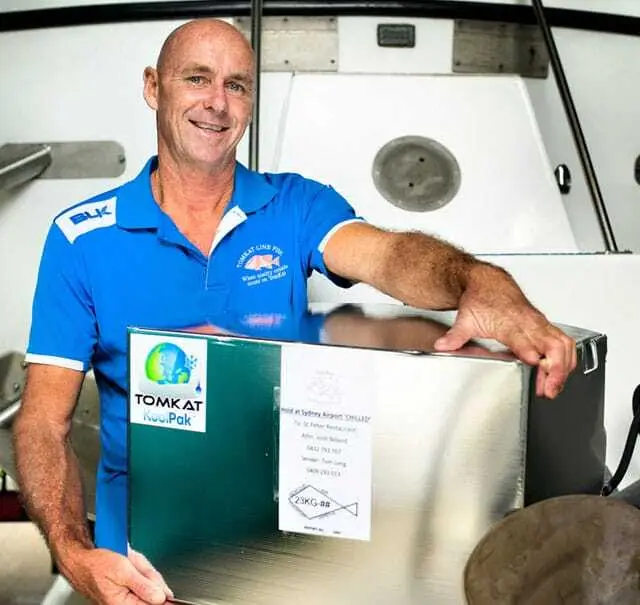

TomKat Fish Line has developed a thermally insulated container equipped with an NFC temperature sensor tag from SAG. The KoolPak container the enables the track and trace of temperature-sensitive goods like seafood across the supply chain. Both counterfeit protection and temperature monitoring is made possible with the NFC tag. This is used in combination with gate scanning equipment from Feig Electronic and a specially developed software.
TomKat Fish Line has developed a thermally insulated container equipped with an NFC temperature sensor tag from SAG. The KoolPak container the enables the track and trace of temperature-sensitive goods like seafood across the supply chain. Both counterfeit protection and temperature monitoring is made possible with the NFC tag. This is used in combination with gate scanning equipment from Feig Electronic and a specially developed software.

"We gave a lot of thought at the start of the project about how we were going to provide traceability with the KoolPak. We’ve looked at barcode and QR code technology initially. These technologies proved problematic when the KoolPak was assembled. Then we came across NFC technology and were immediately taken with the its capabilities – especially in combination with the smartphone. We saw early on the value of provenance, where everyone wants to have some recognition where their product has gone or where they’ve been harvested from for example. NFC technology with temperature sensing capabilities was the answer."

Tom Long
COO and Founder
More Stories on NFC Technology
NFC is Becoming Increasingly Important for Industry
Technologies such as NFC (Near Field Communication) play a crucial role in the digitalization of companies today. The Internet of Things (IoT) in conjunction with NFC, plays an important role in this. NFC offers a simple, secure, and efficient method of data transmission that is particularly suitable for IoT applications. This enables companies to digitize and optimize their business processes by intelligently connecting devices and objects.
NFC security is another important aspect that NFC offers in IoT implementations. Since NFC has a very short range and requires physical proximity to the reader, the risk of eavesdropping or unauthorized access is reduced. In addition, many NFC providers offer advanced encryption techniques to ensure that the transmitted data is protected.
Some companies have begun to actively integrate NFC into their digitalization strategies, supported by a growing number of NFC providers developing specialized solutions and services. These providers play a crucial role in enabling companies to transition to smarter and more connected work environments. By providing robust and easy-to-use NFC-based systems, they are helping to unlock the full potential of the Internet of Things, leading to greater efficiency, improved customer experience and ultimately stronger business growth.
The Integration of Sensors in NFC Systems
Sensors can also be easily integrated into systems based on NFC interfaces. The integration of NFC sensor tags, which can store data, capture environmental information and transmit both wirelessly, has many advantages in the application. Convenient readout via smartphone, wireless real-time measurement of a wide range of measured variables and unique identification through globally unique numbering are the major advantages of the small tags.
There are many parameters that can be captured by sensors with an NFC interface. The products from Microsensys, for example, offer a wide range of measured variables that can be read out via NFC, including temperature, humidity and pressure.
- Temperature Sensors NFC tags with integrated temperature sensors can be used, for example, to monitor the storage temperature at various points in the supply chain, especially for perishable and temperature-sensitive products such as food or pharmaceuticals.
- Humidity Sensors These sensors can be integrated into NFC tags to monitor ambient humidity, which can contribute to digitalization in agriculture and transport.
- Pressure Sensors Pressure sensors are particularly used in industry. Here, the NFC interface is ideal for monitoring the condition of packaging, the load on materials or instantaneous pressures on systems (condition monitoring).
Partners Spezialized in NFC Solutions
Trends in NFC Technology
NFC will play an increasingly important role in mobile payments. This is partly due to consumer acceptance and partly due to the growing number of contactless payments, and digital wallets such as Apple Pay, Google Wallet, and Samsung Pay.
Another trend is improved security functions, which make the smartphone interesting for authentication such as two-factor authentication systems and access controls. This is supported by advancing encryption and secure data transmission.
In the future, NFC will also play an important role in the communication between networked devices in the IoT ecosystem. This includes the simple pairing and configuration of smart home devices.
Further Developments in NFC Technology
Future NFC standards could enable higher data transfer rates and a greater range, which would expand the number of applications. The combination of NFC with UHF RFID, 5G, and edge computing technologies will enable real-time interactions. NFC can also be integrated into AR applications to connect physical and digital worlds and create interactive experiences.
Thanks to the possibility of energy transfer, NFC is also suitable for intelligent energy exchange between devices; this technology is called NFC charging. NFC tags can be used for real-time tracking and for the management of supply chains to increase efficiency and transparency. NFC sensors could also be used to monitor temperature and other environmental conditions in cold chains.