What is Counterfeit Protection?
The term "counterfeit protection", also known as "anti-counterfeiting", refers to the measures and technologies used to prevent the manufacture, distribution, and sale of counterfeit or pirated goods.
Anti-counterfeiting measures include serialization and track & trace, chemical and industrial identification, smart packaging, and the use of authentication solutions and tamper-proofing technologies such as RFID, NFC, QR codes, barcodes, blockchain, IoT sensors, and GPS. These measures employ specialized security elements and security features. Ensuring conformity to standards is crucial. ISO standard 12931, published in 2012, and ISO standard 22381, published in 2018, are guidelines created for the implementation of anti-counterfeiting solutions.
Anti-counterfeiting measures are used in various industries. These include the healthcare and pharmaceutical industry, the automotive industry, retail, and industrial manufacturing. The aim of anti-counterfeiting is to prevent damage to brand reputation and potential risks to consumers, and to reduce the loss of revenue for legitimate businesses.
What Are Counterfeits?
A counterfeit or falsified product is an object or information that has been deliberately produced or manipulated with the purpose of deception. Counterfeit products are imitations that are usually of inferior quality. The use or consumption of certain counterfeit products, such as medicine or car parts, can pose a significant risk to the end consumer. This ultimately leads to a negative impact on the brand image. The dangers of counterfeit products is one of the main reasons why anti-counterfeiting measures are so important.
Counterfeit products are manufactured from various countries, including China, Hong Kong, Singapore, and the United Arab Emirates. Products that are commonly counterfeited include clothing, accessories, medicine, car licenses and identification cards, car and airplane parts, electronics, and more.
Wireless IoT Technologies and Counterfeit Protection
Products for an Anti-Counterfeiting System
IoT products used to build an anti-counterfeiting system can include NFC and RFID tags and readers, GPS trackers, IoT sensors, and blockchain technologies. Data carriers are attached to original products or packaging. These are read either with mobile or stationary wireless RFID readers, or with NFC-enabled smartphones.
Authentication apps are also used to enable consumers to check the authenticity of products. The apps scan the RFID or NFC tags and connect to a central system. IoT gateways are also frequently used to collect data from the data carriers. Cloud-based platforms are used to collect and process data from IoT gateways.
Blockchain can provide a record of product transactions. For high-value products, GPS trackers can be integrated on the packaging or on the products themselves to enable real-time location tracking. Various IoT sensors can be integrated into products or on packaging to monitor temperature and humidity fluctuations, for example. Any deviation from the preset parameters can trigger a warning that indicates possible tampering or counterfeiting.
Facts & Figures
The economic impact of counterfeit products is enormous. According to a study by the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) and the European Union Intellectual Property Office (EUIPO), global trade in counterfeit and pirated goods was worth up to 509 billion USD in 2016, which corresponds to around 3.3 percent of global trade. In 2019, counterfeit and pirated products accounted for 5.8 percent of EU imports. This corresponds to a value of around 119 billion Euros.
According to a study published in the Pharmaceut Med. journal, for example, counterfeit pharmaceuticals alone generate up to 200 billion USD annually worldwide. The same study reports that the World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that around 1 million people die each year from consuming counterfeit medication.
Real-World Examples of Counterfeit Protection with IoT
The future need for anti-counterfeiting measures stems from the increasing complexity of global supply chains, rising economic impact, concerns for consumer safety, and public health, the sophistication of counterfeits, and the importance of brand reputation and regulatory compliance.
IoT technologies offer innovative solutions to address these challenges by improving authentication, track and traceability, and security, ultimately protecting consumers, businesses, and society. The following success stories from real-world economy show the use cases that are possible with wireless IoT technologies in the retail, automotive, and healthcare sectors, for example.
Counterfeit Protection at Collectors Universe
The American company Collectors Universe uses HID's Trusted Tag Services to verify the authenticity of collectibles such as coins, trading cards, sports memorabilia, and autographs. Collectible coins are usually enclosed in packaging with a PCGS (Professional Coin Grading Service) label. In a pilot phase, NFC tags were embedded in the card holders of approximately 100,000 coins behind the PCGS label. Collectors read the NFC tags with an NFC-enabled smartphone. This allows collectors to authenticate the coin via the cloud-based authentication platform Cloud Authentication Service.
"Collectors Universe is the first company in the field of numismatic collectibles to technologically secure counterfeit protection on a large scale with HID Trusted Tag Services. Ensuring the authenticity, certification and grading of collectibles is critical."
Counterfeit Protection in the Cayman Islands
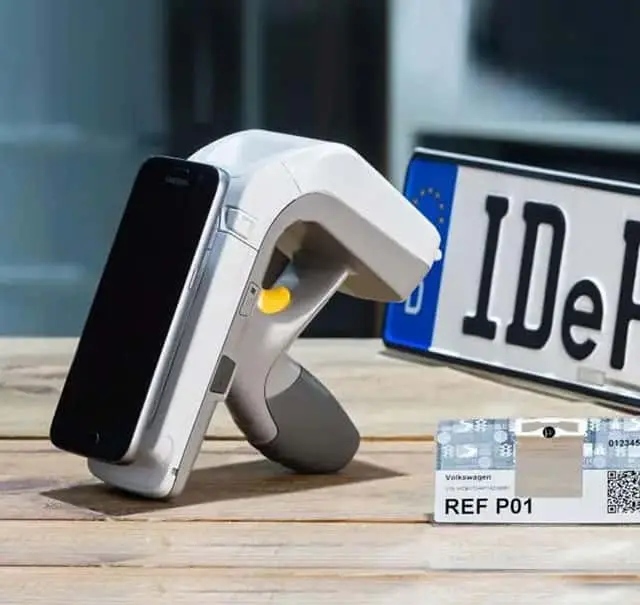

All vehicles in the Cayman Islands are equipped with RFID technology for vehicle identification. The rollout began in 2016. The Caymanian Department of Vehicles & Drivers' Licensing (DVDL) received 90,000 IdePLATES and 45,000 IdeSTIX from Tönnjes. 10 stationary reading points have been installed at specific locations such as bridges and tunnels. 50 mobile devices are used by the police to access the central database of the registration authority. During traffic checks, the data from the RFID chip embedded in the license plate is transmitted to the smartphone. The RFID tags are completely forgery and theft-proof and serve as a unique ID card for each vehicle.
All vehicles in the Cayman Islands are equipped with RFID technology for vehicle identification. The rollout began in 2016. The Caymanian Department of Vehicles & Drivers' Licensing (DVDL) received 90,000 IdePLATES and 45,000 IdeSTIX from Tönnjes. 10 stationary reading points have been installed at specific locations such as bridges and tunnels. 50 mobile devices are used by the police to access the central database of the registration authority. During traffic checks, the data from the RFID chip embedded in the license plate is transmitted to the smartphone. The RFID tags are completely forgery and theft-proof and serve as a unique ID card for each vehicle.

“The DVDL is very proud of what they have achieved. In principle, any country can use our system. Once you start thinking digitally, RFID-based electronic vehicle management is a solution for every country.“

Olaf Renz
Managing Director
Counterfeit Protection of Components at Hasco

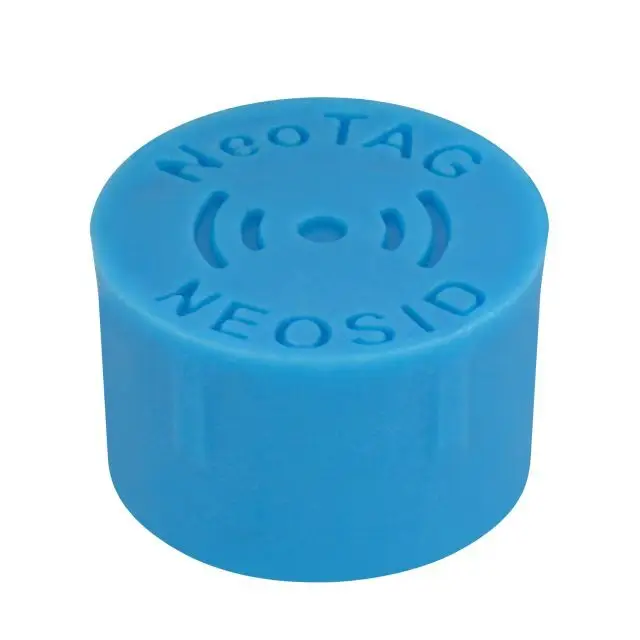
The standard components specialist Hasco has been integrating RFID into its two-stage ejectors as an anti-counterfeiting measure since 2023. All two-stage ejectors are equipped with an 8 millimeter RFID mould tag from Neosid from the production stage onwards. The RFID tag contains unique information for each product. This includes product animations, order designation, CAD data, product type, material number and maximum mold size. This gives each component a unique ID. With the Hasco app, customers scan the RFID tag using an NFC-enabled smartphone or RFID reader. Verification of the component's originality is then displayed in the app.
The standard components specialist Hasco has been integrating RFID into its two-stage ejectors as an anti-counterfeiting measure since 2023. All two-stage ejectors are equipped with an 8 millimeter RFID mould tag from Neosid from the production stage onwards. The RFID tag contains unique information for each product. This includes product animations, order designation, CAD data, product type, material number and maximum mold size. This gives each component a unique ID. With the Hasco app, customers scan the RFID tag using an NFC-enabled smartphone or RFID reader. Verification of the component's originality is then displayed in the app.

"The project arose from dialog with customers. We were repeatedly asked whether it would be possible to link 3D data, installation instructions or maintenance instructions directly to the product in order to reduce the need to search for documentation. We are now receiving recognition and positive feedback from customers. The "aha effect" has occurred."

Alexander Ulman
Team Leader and Product Manager
More Stories on Counterfeit Protection
The Future of Counterfeit Protection
Growing interest in circularity and sustainability for companies is driving consumers towards alternative purchasing and consumption options, such as buying second-hand items and renting. This will result in increased opportunities for counterfeiters. As a result, brands will need to turn to AI and machine learning in order to distinguish between sophisticated counterfeits and vintage goods that are authentic. Furthermore, using AI in companies enables predictive analytics which can foresee possible counterfeiting attempts, allowing companies to take proactive measures.
Smart packaging is also considered a future trend as a counterfeit protection measure. These intelligent packaging solutions offer invisible signatures and can facilitate direct interaction with consumers via smartphones. This will enable the authentication of products in real-time.
Governments and regulatory agencies are ramping up their anti-counterfeiting efforts through strict policies and technological advancements on a global scale. Joint efforts between the public and private sectors are encouraging the creation and adoption of standardized anti-counterfeiting strategies, strengthening worldwide enforcement and protection.
The Advantages of IoT-Based Counterfeit Protection
Advantages of Wireless IoT
- Real-time monitoring
- Real-time product authentication and verification
- Increased customer loyalty and trust
- Increased supply chain transparency
- Optimized product traceability
By embedding IoT devices such as an RFID tag, NFC chip or sensors in products, companies can build a complex network for real-time monitoring and traceability throughout the supply chain. This increased transparency enables the rapid detection and prevention of counterfeit products. This way, consumers are protected from potentially harmful or inferior products.
In addition, the IoT facilitates robust authentication mechanisms that allow stakeholders to instantly verify product authenticity using smartphones or specialized readers. Beyond authentication, the wealth of data collected by IoT devices enables advanced analytics and insights. This allows companies to identify counterfeiting patterns and anomalies and develop proactive intervention strategies.
IoT also promotes transparency and digitalization in the supply chain, reduces operational costs, and increases consumer trust and engagement. Ultimately, the potential of IoT for anti-counterfeiting lies in its ability to revolutionize product authentication, traceability, and consumer protection, thereby protecting brand integrity and promoting a safer, more transparent marketplace.
By embedding IoT devices such as an RFID tag, NFC chip or sensors in products, companies can build a complex network for real-time monitoring and traceability throughout the supply chain. This increased transparency enables the rapid detection and prevention of counterfeit products. This way, consumers are protected from potentially harmful or inferior products.
In addition, the IoT facilitates robust authentication mechanisms that allow stakeholders to instantly verify product authenticity using smartphones or specialized readers. Beyond authentication, the wealth of data collected by IoT devices enables advanced analytics and insights. This allows companies to identify counterfeiting patterns and anomalies and develop proactive intervention strategies.
IoT also promotes transparency and digitalization in the supply chain, reduces operational costs, and increases consumer trust and engagement. Ultimately, the potential of IoT for anti-counterfeiting lies in its ability to revolutionize product authentication, traceability, and consumer protection, thereby protecting brand integrity and promoting a safer, more transparent marketplace.
Advantages of Wireless IoT
- Real-time monitoring
- Real-time product authentication and verification
- Increased customer loyalty and trust
- Increased supply chain transparency
- Optimized product traceability
The Challenges of IoT Anti-Counterfeiting
Implementing IoT anti-counterfeiting measures poses several challenges for organizations to effectively overcome. One major challenge is the initial investment and set-up costs required to deploy IoT infrastructure, including sensors, RFID tags, and data analytics systems. In addition, ensuring interoperability and compatibility between different IoT devices and platforms can be complex, especially in global supply chains involving multiple players.
Furthermore, maintaining the security and integrity of IoT data is very important, as counterfeiters may attempt to intercept or manipulate the information to avoid detection. Additionally, the enormous amount of data generated by IoT devices poses a challenge for storage, processing and analysis and requires a robust IT infrastructure and capabilities.
Regulatory compliance and privacy concerns related to the collection and use of personal data further complicate the implementation of IoT-based anti-counterfeiting measures.
Overcoming these challenges requires careful planning, investment in technology and talent, collaboration between all stakeholders, and compliance with cybersecurity and data management measures.
Partners Spezialized in Anti-Counterfeiting Solutions
Outlook – Next-Level Anti-Counterfeiting Measures
The future of anti-counterfeiting will see remarkable progress thanks to new trends such as nanotechnology and microtagging, as well as the integration of machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI).
Nanotechnology and Micro Labeling
Nanotechnology enables the production of microscopic labels or markings that are almost impossible to copy and offer a high level of security against counterfeiting. These micro-labels can be embedded in products or packaging and detected with special devices, enabling covert authentication.
Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence
Advanced analytics techniques, including machine learning and artificial intelligence, are increasingly being used to detect counterfeiting patterns and anomalies in large data sets. By analyzing historical data and detecting subtle patterns indicative of counterfeiting activity, machine learning algorithms can improve the effectiveness of anti-counterfeiting measures.