What is a Traditional Supply Chain?
The concept of the supply chain stems from economics. The supply chain comprises the following stages: Procurement, production, warehousing and order picking, transportation and logistics chain management, distribution, and returns management. The coordination of these processes is complex, as it links numerous players, logistics managers, and resources.
Traditional supply chains are linear, moving goods in a sequential manner from suppliers to manufacturers, then to distributors, retailers, and finally to the customers. There is limited integration and communication between different entities in the traditional supply chain. Each stage often operates independently with minimal information sharing. Logistics management tools are not used and documentation involves paperwork rather than digitized records. The focus of a traditional supply chain is to reduce cost investment through the optimization of operational efficiency in production and shipment.
Why is a Digitized Supply Chain so Important?
The key word here is “disruption”. Disruptions in the supply chain can be caused by natural and man-made disasters, pandemics, cyberattacks, politics, transportation and supplier issues, as well as inventory and labor shortages, for example. Events that caused supply chain disruptions include the China-United States trade war in 2018, the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, the semiconductor shortage in 2020, the Russia-Ukraine War in 2022, and the Panama Canal drought in 2023.
Supply chain disruptions result in restricted or halted production, financial losses, and customer dissatisfaction on a global scale. A quick response to supply chain disruptions is a must for companies today, in order to avoid bottlenecks, delays, and other unwanted situations. Traditional supply chains are often not flexible, and are unable to adapt to supply chain disruptions.
Companies must therefore build resilient supply chains in order to be able to respond to such disruptions. How? The methods include developing a risk-awareness strategy and establishing a risk-mitigation plan. Companies should also implement a proactive monitoring system based on real-time data analytics to detect potential problems in advance. It is also important to maintain open communication between all supply chain stakeholders. This can be achieved by investing in technologies such as supply chain visibility software, automated systems, and predictive analytics.
The investment in technology solutions that provide real-time data is crucial in enabling resilient supply chains. Examples of such solutions include RFID in the supply chain and GPS tracking. The key is to optimize supply chain visibility, and thus, improve transparency. By ensuring that goods are visible throughout the supply chain, companies know the location and status of their goods, and also learn of any potential risks. This allows companies to act at an early stage to mitigate any potential disruptions. For this reason, a digitized supply chain is often synonymous with a resilient supply chain.
Digitized Supply Chains and Supply Chain Management (SCM)
The introduction of Supply Chain Management 4.0 involves the complete digitalization of the supply chain. A digital transformation of the supply chain is often part of Industry 4.0 and involves the integration of advanced technologies. This includes the Internet of Things (IoT) in the supply chain, artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, cloud computing, advanced analytics, Robotics Process Automation (RPA), digital twins, edge computing in the supply chain, supply chain control towers, 3D printing, as well as drones and autonomous vehicles, for example. The key is to connect the network of assets, data, and operations through supply chain management (SCM).
SCM management ensures the control and coordination of all phases of the supply chain: planning, sourcing, production, distribution, and returns. The SCM process includes demand management, SCM supply management, the monthly integrated business management process S&OP, and product portfolio management. Companies today use a variety of tools and technologies in supply chain management to make processes more efficient, reduce costs, and optimize workflows:
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems integrate various business processes such as purchasing, production, sales, and finance into a standardized framework. Specialized supply chain management (SCM) software controls the entire supply chain with modules for demand planning, inventory management, and transport planning. Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) and Transportation Management Systems (TMS) enable the precise control of warehousing and transportation.
Wireless SCM, powered by IoT technologies, has fundamentally changed the way companies manage and control their supply chains. SCM SAW sensor tags and supply chain IoT (wireless supply chain) provide real-time data for inventory tracking and the monitoring of the manufacturing chain. How does 5G work in the supply chain? 5G has the potential to optimize real-time tracking of assets due to increased data transmission capabilities in the supply chain.
SCM RFID tags can transmit information wirelessly and enable automated identification and tracking of products. SCM with NFC technology ensures fast and secure wireless communication between devices in the immediate vicinity. This simplifies the capture and tracking of goods as they move through the supply chain. Products can be equipped with NFC tags to track their location and status in real time.
Demand forecasts, identification of bottlenecks and optimized stock levels are made possible by artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). Supply chain blockchain technology improves the transparency, as well as the track and traceability of individual products. Supply chain big data solutions are used to analyze data volumes to identify trends and optimize processes. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) enables the automation of routine tasks. These technologies increase the efficiency and flexibility of modern supply chains.
Another important aspect of the digitized supply chain is OCR (Optical Character Recognition) technology. OCR in the supply chain automates data acquisition and processing. The result: More efficient management of documents and information along the supply chain. This not only reduces the workload, but also minimizes human error and accelerates the execution of supply chain processes. The digitization of SCM not only promises improved efficiency and transparency, but also opens up new opportunities for innovative business models and partnerships.
What Types of Supply Chains Are There?
Companies that want to build supply chains need to understand the different types of supply chains. Here are the seven main supply chain models.
1. Agile Model
The focus of an agile supply chain lies on process efficiency and empowered employees. It is an active system that allows companies to keep track of stock, while also anticipating future demands. The key is to enable employees the ability to collect and share accurate and real-time information. For this reason, companies using an agile supply chain model often invest in data-driven processes and modern technologies. This allows companies to have better control over their supply chain. Real-time data and communication enables quick decision-making. This makes it able to quickly respond to unexpected changes in supply and demand. An agile supply chain is ideal for companies that deal with highly variable customer demand. The company Nike uses this supply chain model, for example.
2. Continuous Flow Model
This supply chain enables the constant delivery of products with minimal pauses in the flow of supply. This results in quick and reliable deliveries and improved customer service. The key is to maintain a steady supply and thus, maximize efficiency. In other words, a continuous flow supply chain relies on the stability of supply and demand. This model is ideal for companies that have consistent production processes. The companies Amazon, Apple, PepsiCo, and Coca-Cola, for example, use this supply chain model.
3. Custom-Configured Model
As it’s name suggests, companies using this model customize their supply chains according to the needs or demands of their customers. Companies using this model require a high level of communication with customers. This model is ideal for companies that offer specialized products or services. The company Dell uses this supply chain model. The company offers individualized computer configurations according to individual customer needs.
4. Efficient Chain Model
The focus of an efficient chain supply chain lies on the reduction of waste and on maximizing supply chain efficiency. Companies using this model require accurate production forecasts in order to prepare only the raw materials and machinery that are required. An efficient chain supply chain is ideal for large-scale production processes that prioritize high volume production and low production costs. This model is, however, vulnerable to disruptions like shortages in labor and raw materials, for example. This may lead to delays in the supply chain and the resulting costs. The companies Toyota, General Mills, and McDonald’s use this model, for example.
5. Fast Chain Model
Companies with product lines that have short life cycles use the fast chain model. The focus is on speed – ensuring quick deliveries and response to supply and demand. This model is ideal for companies that deal with seasonal trends. This includes fashion retailers and electronics manufacturers, for example. The companies Zara, Gap, Adidas, and Kenneth Cole use this model.
6. Flexible Model
Companies using this model focus on flexible supply chain operations. The key is the ability to adapt to sudden changes in order to meet customer demands. This model is ideal for companies that need to adjust production levels according to seasonal demand. The companies Hewlett Packard and Office Depot use this model. Agricultural businesses, for example, adapt their supply chains to seasonal crop yields.
7. Virtual Model
The virtual supply chain is an emerging model. This model involves the use of virtual technologies to optimize supply chain operations. This includes cloud computing and data analytics. The result: Increased visibility, communication, efficiency, and flexibility in the supply chain. The company Proctor & Gamble uses this model, for example.
Wireless IoT Technologies and Supply Chain
IoT Products for the Supply Chain
Various IoT products are used in supply chain management to enable efficient data collection and tracking.
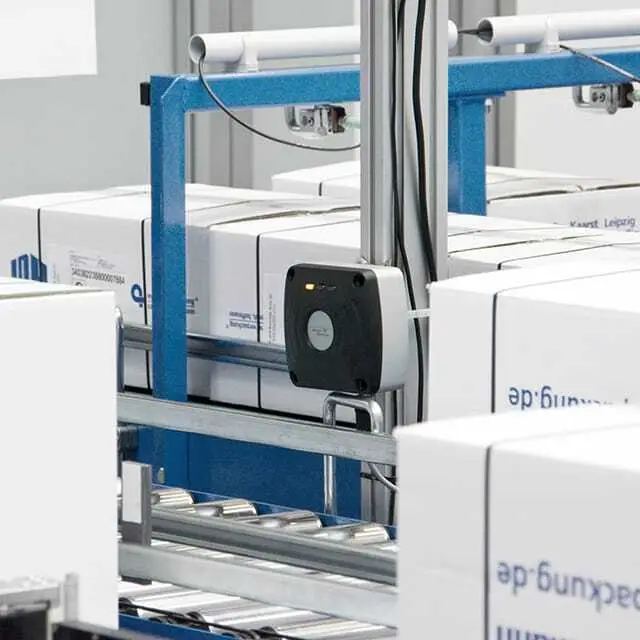
Data carriers such as NFC and RFID tags and transponders can be attached to products from production. These data carriers store important information about products and enable seamless tracking throughout the supply chain. Specialized printers enable the rapid creation of supply chain barcode and RFID labels for industrial identification and the tracking of goods.
RFID read/write devices, as well as barcode scanners and RFID scanners, are used for the quick capture of product information and to automate processes such as inventory management, receiving, and shipping. In combination with RFID systems, antennas enable RFID tag information to be captured over longer distances and thus, support the automation of tracking processes. NFC-enabled readers or smartphones are used to read NFC tags.
BLE gateways collect data from BLE beacons or sensors attached to goods or means of transportation. They then transmit this data to central systems for further analysis. Supply chain GPS trackers and IoT-based tracking devices are used to monitor the position and condition of goods during transportation in real time. RTLS (Real-Time Localization) systems in warehouses can be set up with anchors, tags, sensors, and software platforms, for example.
Surveillance cameras are used for the security and protection of plants. Specialized cameras are also used for optical inspection and quality assurance of products.
Software solutions for supply chain management, warehouse management systems (WMS), enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, and specialized tracking and analysis tools are used to integrate and analyze the data collected by the various devices and technologies.
Facts & Figures
Supply chain disruptions are common and result in major losses for companies. According to a report by the market research platform “Gitnux”, supply chain disruptions typically result in a 3-5 percent increase in costs, and a 7 percent decrease in total sales. Over 80 percent of companies have experienced a disruption in the supply chain in the past 12 months.
This shows the importance of resilient supply chains. Over 50 percent of companies believe that increasing automation and digitization initiatives will enhance supply chain resilience. The use of robotics in the supply chain is expected the grow by 14 percent globally by 2025. This shows the automation potential of supply chains. According to a report by “World Metrics”, 62 percent of companies already use some form of advanced supply chain analytics. 93 percent of freight forwarders and 98 percent of third-party logistics companies believe that data-driven decision-making is critical to supply chain operations.
Successful Examples of IoT in the Supply Chain
There are numerous use cases where companies have deployed advanced technologies in the supply chain.
A company using IoT sensors to track the temperature of perishable goods can reroute shipments if a sensor indicates a temperature breach, preventing spoilage. Retailers like Walmart use AI and ML to optimize inventory management, ensuring that products are available where and when they are needed, even during disruptions. Companies like IBM and Maersk have developed blockchain solutions to enhance the transparency and efficiency of global shipping logistics. Firms like Amazon use cloud-based supply chain management solutions to enable real-time tracking and coordination of their vast logistics networks. A manufacturer using predictive analytics can foresee potential supply chain bottlenecks due to geopolitical issues and adjust sourcing strategies accordingly. Companies like General Electric (GE) use digital twins to simulate the performance of their supply chain, allowing them to test and implement disruption response strategies effectively.
The following solutions are based on real success stories and demonstrate the benefits of IoT integration in the food retail and logistics supply chain.
Food Supply Chain Tracking at Granterre

The Italian food group Granterre is using an RFID tracking solution to ensure visibility in the food supply chain at its 30,000 square meter distribution center in Bologna Interporto. Transport units are fitted with RFID tags from production and automatically captured via RFID gates at the entrance and exit of the center. Murata's id-Bridge 4.0 middleware controls the RFID system. The result: A 50 percent reduction in loading and unloading times and a shipping accuracy of 99.95 percent.
The Italian food group Granterre is using an RFID tracking solution to ensure visibility in the food supply chain at its 30,000 square meter distribution center in Bologna Interporto. Transport units are fitted with RFID tags from production and automatically captured via RFID gates at the entrance and exit of the center. Murata's id-Bridge 4.0 middleware controls the RFID system. The result: A 50 percent reduction in loading and unloading times and a shipping accuracy of 99.95 percent.

Supply Chain Tracking with NXP Semiconductors

Food logistics in the fruit and vegetable sector places high demands on quality standards. With UHF RFID solutions, such as the UCODE chips from NXP Semiconductor, all fruit and vegetable containers can be tracked in real time within the supply chain. This ensures the freshness and quality of fruit and vegetables. By labeling the units with UHF RFID and using a merchandise management system, older food products can be positioned in the warehouse so that they are sold more quickly. The result: Greater customer satisfaction.
Food logistics in the fruit and vegetable sector places high demands on quality standards. With UHF RFID solutions, such as the UCODE chips from NXP Semiconductor, all fruit and vegetable containers can be tracked in real time within the supply chain. This ensures the freshness and quality of fruit and vegetables. By labeling the units with UHF RFID and using a merchandise management system, older food products can be positioned in the warehouse so that they are sold more quickly. The result: Greater customer satisfaction.

Track & Trace in the Supply Chain at TomKat
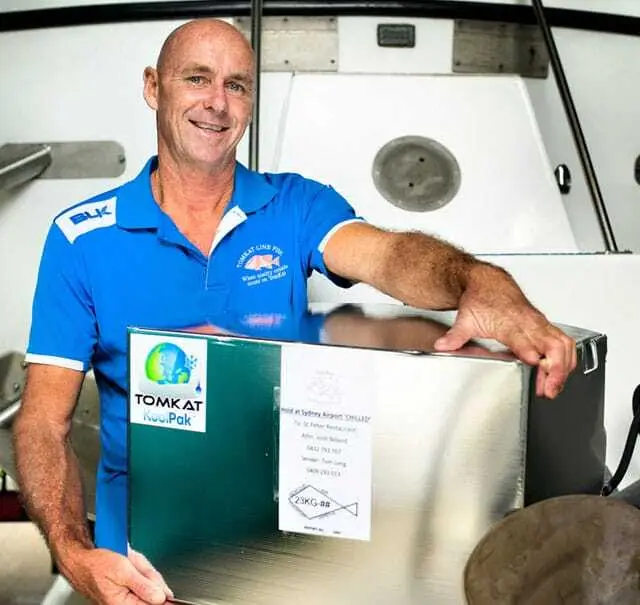

With an NFC-based container tracking solution, temperature-sensitive goods such as seafood can be fully traced throughout the cold chain and supply chain. The KoolPak developed by TomKat is a thermally insulated container equipped with an NFC temperature sensor tag from SAG. This tag enables both temperature monitoring and counterfeit protection. Customers can monitor the KoolPak throughout the supply chain using specially developed software and gate scanning equipment from Feig Electronic.
With an NFC-based container tracking solution, temperature-sensitive goods such as seafood can be fully traced throughout the cold chain and supply chain. The KoolPak developed by TomKat is a thermally insulated container equipped with an NFC temperature sensor tag from SAG. This tag enables both temperature monitoring and counterfeit protection. Customers can monitor the KoolPak throughout the supply chain using specially developed software and gate scanning equipment from Feig Electronic.

“By using the NFC sensor tags and the monitoring software, local fishermen, international customers and official authorities can be sure that the provenance of the products is accounted for. Kath and I see West Africa as an important potential market for the KoolPak for example. The high temperatures there make inland transport of perishable goods challenging. The track and trace function of the NFC tags can be used to detect and prevent fraud and other illegal activities along the supply chain.”

Tom Long
COO and Founder
More Stories on Supply Chain
Step by Step to a Digitized Supply Chain
In recent years, the global supply chain has been significantly disrupted by crises mentioned in the sections above. Due to these disruptions, many companies are increasingly realizing the benefits of an automated and digitized supply chain.
An impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, for example, is the boom in e-commerce, which places high demands on digitalization in retail and the corresponding supply chains. For many companies, increasing transparency in the supply chain is a top priority in order to improve inventory management, increase efficiency, and reduce disruptions. An increasing number of companies are also planning to implement AI solutions for the supply chain as the next step to automation and robotics.
Statistics show that the digitalization of the supply chain is gaining momentum, albeit at a slower pace than in other industries. The main reasons for this are the complexity of supply chains, the use of outdated systems, high investment costs, security concerns and a shortage of skilled workers. Flexible technologies such as cloud solutions and modular systems, cooperation with technology providers and research institutions, as well as training programs are crucial.
Standardization and interoperability facilitate integration. The prerequisite for the successful digitalization of the supply chain is the integration of technologies, processes, and employees.
Just-in-Time (JIS) and Just-in-Sequence Logistics
Modern supply chains are increasingly adopting “Just-in-Time” (JIT) and “Just-in-Sequence” (JIS) logistics methodologies. JIT and JIS are designed to to enhance efficiency and reduce waste. JIT delivery ensures that materials and components arrive exactly when needed in the production process, minimizing inventory levels and storage costs. JIS takes this a step further by ensuring that these materials and components not only arrive on time, but also in the precise order required for production, which is particularly useful in complex manufacturing environments like the automotive industry.
These methodologies are integral to modern supply chains as they promote lean manufacturing, improve coordination and synchronization with suppliers, and leverage advanced technology for real-time data sharing and automation. By reducing excess inventory and optimizing the flow of goods, JIT and JIS contribute to more responsive, flexible, cost-effective, and sustainable supply chain operations.
Kanban
Kanban is an example of a widely used workflow management method in modern supply chains for managing inventory and production processes. It emphasizes JIT production, where materials and products are produced or procured only as needed. Kanban is fundamentally a visual management tool that uses cards (or digital signals) to represent work items and their status in the production process.
These cards are typically placed on a Kanban board, which is divided into columns that represent different stages of the workflow (e.g., Requested, In Progress, Done). This visual representation helps teams quickly understand the status of work and identify bottlenecks.
With advancements in technology, many companies have transitioned to digital Kanban systems. These digital platforms offer enhanced capabilities such as real-time tracking, automated notifications, and integration with other enterprise systems like ERP and Material Requirements Planning (MRP). Digital Kanban provides greater visibility and control over the supply chain, enabling quicker decision-making and improved efficiency.
Cold Chain Logistics
The implementation of IoT and RFID in the supply chain has an enormous impact, particularly in the area of cold chain logistics. Cold chain IoT enables the precise monitoring and control of temperature and other relevant parameters during the transport of temperature-sensitive products.
By using IoT devices that continuously capture data such as temperature, humidity, and location, companies can ensure that the cold chain is maintained throughout transportation. This data is then supplemented by cold chain RFID tags, which enable unambiguous identification of the products and ensure complete traceability along the supply chain.
The Advantages of IoT in the Supply Chain
Advantages of Wireless IoT
- Reduced carbon footprint
- Increased customer satisfaction
- Increased supply chain efficiency
- Increased visibility and traceability
- Reduced costs
Increased efficiency in the supply chain is achieved through automation and optimized warehousing. IoT supply chain management is increasingly being used for this purpose. IoT supply chains have many advantages.
IoT devices are the eyes and ears of the supply chain. They monitor the location, movement, and condition of all products that are tagged. This enables enhanced visibility and tracking. The analysis of the data collected by IoT devices improve operations. Processes such as inventory management and shipment tracking become automated. Predictive maintenance (PdM Maintenance) of production equipment also become possible, which prevents production downtimes.
Companies use IoT technologies for the real-time monitoring of inventory. This eliminates overstocking or stockouts. Product replenishment on the shop floor is automated and the right products are always made available at the right time.
Sustainability for companies is an important factor in the digitalization of the supply chain. Part of the sustainability approach in the digital supply chain is the use of autonomous vehicles and improved route management, as well as the reduction of CO2 emissions. Faster delivery times and improved customer service lead to a general increase in customer satisfaction, which is one of the most important end goals of companies that want to digitize their supply chains.
Increased efficiency in the supply chain is achieved through automation and optimized warehousing. IoT supply chain management is increasingly being used for this purpose. IoT supply chains have many advantages.
IoT devices are the eyes and ears of the supply chain. They monitor the location, movement, and condition of all products that are tagged. This enables enhanced visibility and tracking. The analysis of the data collected by IoT devices improve operations. Processes such as inventory management and shipment tracking become automated. Predictive maintenance (PdM Maintenance) of production equipment also become possible, which prevents production downtimes.
Companies use IoT technologies for the real-time monitoring of inventory. This eliminates overstocking or stockouts. Product replenishment on the shop floor is automated and the right products are always made available at the right time.
Sustainability for companies is an important factor in the digitalization of the supply chain. Part of the sustainability approach in the digital supply chain is the use of autonomous vehicles and improved route management, as well as the reduction of CO2 emissions. Faster delivery times and improved customer service lead to a general increase in customer satisfaction, which is one of the most important end goals of companies that want to digitize their supply chains.
Advantages of Wireless IoT
- Reduced carbon footprint
- Increased customer satisfaction
- Increased supply chain efficiency
- Increased visibility and traceability
- Reduced costs
Partners Spezialized in Supply Chain Solutions
The Challenges of Digitalization in the Supply Chain
Companies face a number of challenges when it comes to digitizing their supply chains.
Supply chains are made up of different players, all using different systems in different locations. Companies need to break away from information silos and switch to a centralized data solution and information flow. Modern enterprise content management (ECM) systems are generally used for this purpose. These systems should be integrated into the IT infrastructure and be accessible to all employees throughout the supply chain.
Another challenge is data management and security. The various players in the supply chain, including manufacturers, logistics providers, suppliers, and end customers, must be able to exchange data securely. This process is often vulnerable to cyber-attacks, unauthorized access, and data breaches. Sensitive information must also be protected. Companies must use secure data exchange protocols, communication channels, and encryption techniques to avoid security breaches in data traffic.
The digitalization of supply chains can also be costly. Significant investments are required in terms of technology, infrastructure, and employee training. However, the value of digitizing supply chains usually outweighs the initial costs. Another challenge relates to the acceptance of technologies by employees, who may be reluctant to adopt new digital systems. For this reason, user-friendly solutions and appropriate training are required. The integration of new digital infrastructures and systems throughout the supply chain in combination with existing systems, processes and technologies can be complex and time-consuming.
Outlook – Next-Level Supply Chain
From AI in companies, to blockchain, and the integration of IoT technologies: These emerging trends show what the future holds in terms of supply chain digitalization.
Generative AI
As a sub-area of AI, generative AI (GenAI) has the potential to take supply chain management, logistics and procurement to the next level. Software engines powered by GenAI can process larger amounts of data. More complex variables can be analyzed. GenAI learns the specific characteristics of a supply chain ecosystem and produces better analyses in the long term.
Blockchain
With the increasing demand for visibility and transparency in the supply chain, blockchain is becoming a trend for the digital supply chain. RFID blockchain enables the logging of all transactions within the supply chain, for example. This improves material tracking throughout the supply chain, reduces paperwork, increases security and transparency and prevents fraud attempts, especially for high-value goods.
IoT
More and more IoT technologies and devices are being used to digitize and automate supply chains. These include RFID, UWB, RTLS, Barcodes, and BLE, for example. The use of IoT technologies optimizes warehouse management, fleet management, inventory management, and maintenance throughout the supply chain.





-6-9-23-responsive.webp)