What Are Wireless RFID Readers?
RFID readers are wireless devices that are used to communicate with RFID tags and capture the data they transmit. They are also called “RFID interrogators”. An RFID reader/writer is able to both read and write data stored on RFID tags.
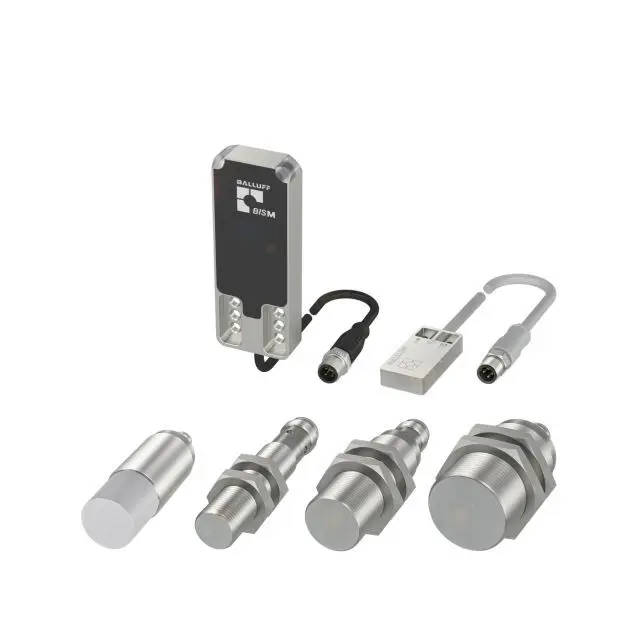
The most basic components of an RFID reader include the processor, antenna connectors, power supply, memory, and a case surrounding an RFID reader module. An RFID reader module is a component of RFID readers that are custom developed. A UHF RFID reader module for example, is part of a customized UHF RFID reader.
RFID readers can either be stationary, mobile, or vehicle-mounted.
A mobile RFID reader, also called an RFID handheld reader, is a portable device that is carried around by workers. Mobile readers are typically equipped with ergonomic designs, rechargeable batteries, and often integrate other functionalities like barcode scanning and wireless communication (Wi-Fi, Bluetooth). Smartphones equipped with RFID scanners can become smartphone RFID readers. In order to pair the smartphone with the RFID scanner, an RFID sled is used.
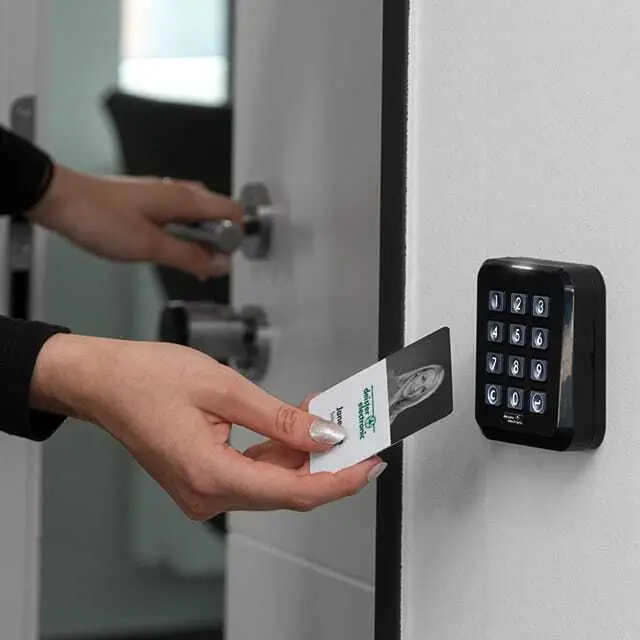
Stationary readers, also known as fixed readers, are positioned in fixed locations to provide continuous and automated data collection. Fixed RFID readers can be placed on gates, walls, or ceilings, for example. Fixed RFID readers are usually more powerful than mobile RFID readers. They often have greater read ranges and are able to connect multiple antennas to cover larger areas or specific zones. Fixed RFID readers are often used to create RFID gates as part of an access control solution.
Vehicle-mounted RFID readers are installed on vehicles like forklifts, trucks, or cranes, for example. By mounting RFID readers on vehicles, operators can automatically capture data on tagged items as they move through different areas. This improves the efficiency of loading, unloading, and transporting goods. Vehicle-mounted RFID readers are typically robust and designed to withstand harsh conditions, including vibrations, extreme temperatures, and dust.
How Do Wireless RFID Readers Work?
RFID readers have antennas that emit radio wave signals. As a result, an electromagnetic field is created. These signals are used to power passive RFID chips which then transfer modulated data to the RFID reader. For active RFID chips, these signals are only used for data transmission, since the chips are powered by a battery instead. Data from the RFID chip is captured by the antenna of the RFID reader.
An RF module in the RFID reader demodulates the signal in order to extract encoded data from the RFID chip. The micro-controller or processor within the RFID reader processes the extracted data and converts it into a data format that is readable. In a final step, the data is sent to connected computer systems or devices through the communication interface, where it can be stored, further processed, and used for various applications, such as updating inventory records, controlling access, or tracking assets.
RFID readers can read multiple RFID tags and RFID labels at the same time, without line of sight. This is known as bulk reading.
Different RFID systems use different frequency bands, each with distinct characteristics that affect their read range, speed of communication, and suitable applications. There are three kinds of frequencies that can be read by RFID readers:
- Low Frequency (LF) | 125-134 KHz
- High Frequency (HF) | 13.56 MHz
- Ultra-High Frequency (UHF) | 865-960 MHz
The read range of an RFID tag or label depends on the frequency band. LF RFID tags can be read at ranges of up to 10 centimeters. The read range of HF RFID tags is up to 30 centimeters. A UHF RFID reader can capture signals from UHF RFID tags at ranges of up to six meters.
Other Wireless Readers
Aside from regular RFID readers, there are many different types of wireless readers. This includes readers that have both Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) and RFID functionalities (BLE RFID readers), and industrial NFC readers, for example.
Another example is an RFID/NFC reader with integrated LoRaWAN technology. This reader is a kind of LoRaWAN RFID reader. A LoRaWAN receiver is designed to receive data transmitted over LoRaWAN. Ultra-Wide Band (UWB) readers capture signals from UWB tags. These devices are commonly used in positioning applications.
Wireless IoT Technologies
RFID Reader Products
Applications That Use Wireless RFID Readers
RFID readers are a part of many applications.
Mobile RFID readers allow users to move freely while scanning RFID tags. This makes them ideal for applications that require mobility, such as inventory control and asset tracking. This applies to all industries that require IoT asset management, such as retail, healthcare, production, automotive, construction, and logistics, for example.
Fixed RFID readers are commonly used in environments where constant monitoring is required. This includes production lines, warehouse entrances and exits, and retail checkout points. These readers are used as part of warehouse management and access control solutions in buildings. Fixed RFID readers are also often used as part of authentication solutions. These readers are used to identify employees in an office building in order to grant them access into certain rooms or areas, for example.
Some warehouse and production lines use a combination different reader types. Handheld, fixed, and vehicle-mounted readers can be used at different stages of a production line, for example.
Example 1: RFID Readers at Toro Aluminium

Toro Aluminium, a Canadian window and door supplier uses UHF RFID solution to ensure correct deliveries of windows to construction sites. A total of 17 fixed readers, 35 antennas, and 10 handheld readers are used. Windows are equipped with UHF RFID tags from production. Both ceiling antennas from Feig Electronic and RFID antennas from Times-7 are used to track the movement of each window. On the construction site, customers use an RFID handheld to check the completeness of the delivery.
Toro Aluminium, a Canadian window and door supplier uses UHF RFID solution to ensure correct deliveries of windows to construction sites. A total of 17 fixed readers, 35 antennas, and 10 handheld readers are used. Windows are equipped with UHF RFID tags from production. Both ceiling antennas from Feig Electronic and RFID antennas from Times-7 are used to track the movement of each window. On the construction site, customers use an RFID handheld to check the completeness of the delivery.

“All production and logistics processes, all readers and antennas and all generated data are connected to Toro Aluminum's ERP system in real time via RFID to Go and RFID Hub.”

Khaled Elshimy
CEO
Example 2: RFID Readers at Neutripuro
An RFID-based laundry management solution is being used by the laundry company Neutripuro – Lavagens Industriais in Portugal. 30,000 rental laundry items are equipped with UHF RFID tags. Inventory counts are performed via an RFID handheld, or via a cabinet that is equipped with an RFID portal and two UHF RFID antennas. All laundry items are captured and registered. The result: A clear overview of on-site laundry inventory.
For more laundry solutions: HID, deister electronic, Huayuan, and JYL-Tech
“We can manage all the clothes and relevant information within minutes. We simply have to put them in the cabinets with the readers. This way, we can get the information we need very quickly, compared to the past. We have some fixed points for capturing the RFID tags at the entrances and exits. We also have mobile readers.”
Felipe Gameiro
Business Analyst







-6-9-23-responsive.webp)