Digitalization in Sports
Sports itself is defined by physical activities with a playful and competitive character. Sport takes place as recreational and competitive sports. The topic of digitalization in sports stands for the digital mapping of movement sequences, the measurement of fitness values, the evaluation of training results, GPS tracking in soccer, the simulation of training sessions, RFID time recording at running events, and the analysis of movement sequences. On the spectator side, the main focus lies on enhancing the sporting experience through digital opportunities for participation and to increase the convenience of attending sporting events.
The sports production industry acts like a manufacturing industry. The care and transportation of athletes and services for spectators and fans are all about logistics, such as mobility and supply.
Overall, digitalization of companies in the sports sector is about combining sport and technology. Wireless IoT technology in particular, with a focus on wireless sensor technology, optimizes sports operations.
The range of application fields in sports shows that sports is made up of different aspects including competition, events, fitness, health, entertainment, production, and logistics, and therefore a wide variety of wireless IoT solutions are used.
How is the Sports Industry Structured?
The sports industry is very diverse and includes producers, active players, passive participants, and service providers.
The following list shows how diverse the sports industry is. However, it cannot be described as an industry. It is a lucrative economic sector, as it accounts for a large proportion of the leisure sector.
- Sporting goods manufacturers produce, for example, sneakers, sportswear, and sports equipment. However, this segment also includes the fields of ergonomics, mechanics, design, marketing, physiology, materials research, and biomechanics.
- Sales and marketing of equipment and clothing, such as sports equipment, shoes, jerseys, or protective equipment.
- Organization of sports leagues and events in which professional athletes participate. Examples include the German Football League, the NBA, the NFL, and other major international leagues and competitions.
- Sports activities at a non-professional level, including school and club sports, as well as recreational sports. Amateur sports encourages mass participation and is often integrated into local communities and educational institutions.
- Gyms, personal training, yoga studios, pilates, online fitness platforms and other services that focus on physical health and fitness.
- TV stations, radio stations, online streaming services, sports journalism, and all other media formats that report on sports, broadcast sporting events, and produce content relating to sports topics.
- Marketing of sporting events, teams and individual athletes, as well as sponsorship agreements in which companies acquire advertising rights to sports facilities, events, and athletes. This involves the organization and management of sports activities and facilities, including the representation of athletes by agencies, the management of sports facilities, and the organization of events.
- The field of sports science is concerned with the further development and investigation of technologies to improve sports performance including biomechanics, sports psychology, nutritional science, and the development of sports technologies such as wearables and performance analysis tools.
- Operators of stadiums and sports facilities, and rental of commercial space in the vicinity of sporting events.
- Sports physicians and rehabilitation centers that specialize in sports injuries.
Wireless IoT Technologies and Sports
Products Designed for the Sports & Leisure Sector
Various products and tools are used in the sports industry to measure sporting performance and training success, to track players and equipment, or to optimize the spectator experience. For example, RFID tags can be embedded in jerseys or equipment as a counterfeit protection measure, to confirm authenticity. In some cases, Bluetooth LE or RFID tags are also used to monitor athletes' performance by measuring position or speed, for example.
Bluetooth LE and LoRaWAN hardware are often used in conjunction with wearables and sensors to collect real-time health data and performance indicators from athletes. Bluetooth LE is often used in smaller, wearable devices due to its low power consumption, while LoRaWAN is often used in environments where both longer range and lower power consumption are required. Scanners and antennas are used to scan tickets and access authorizations at sporting events. GPS trackers can also be used for the same purpose. Based on the health and fitness data, performance analyses and coaching sessions are created.
Various trackers, often linked to GPS, are also integrated to track the movements and performance of athletes. This data is important for training and performance analysis.
How does 5G work in sports? Adidas is developing sportswear with an integrated 5G mobile phone and display. This will allow athletes to read their training data without a smartphone. In future, the clothing will even be able to generate the electricity required for this itself.
Antennas can also be part of a larger RFID system to track tickets and merchandise. High-resolution cameras are used to record and analyze matches. They also enable the use of video evidence in controversial decisions in many sports. In addition to RFID tags, special labels and transponders are also used in sports equipment and gear to make them easier to track and manage.
Wireless label printers and card production systems are used when tickets, chip cards, or accreditation need to be produced. Software solutions are used to analyze and evaluate the captured data.
5G Connectivity Drives the IoT Sports Market
According to a report by ‘GlobalData’, growth in the IoT market for sports solutions will increase by more than 15 percent between 2022 and 2027. IoT software products and services will account for the largest share.
According to a report by ‘Mordor Intelligence’, revenue growth for wearable IoT devices such as fitness watches or smart sportswear will increase by more than 4 percent between 2024 and 2029. This growth will be driven by increasing demand, advances in communication protocols, and the miniaturization of sensor technology. 5G connectivity, in particular, continues to drive the IoT sports market.
Internet of Things (IoT) in the Sports Industry
The possibilities for process optimization in sports are complex and involve various solutions, application scenarios, and players.
Sportswear
The integration of RFID technology into sports shoes is an innovative application that is becoming increasingly widespread in the sports industry. RFID tags integrated into sports shoes can be used to uniquely identify athletes. This is particularly useful in team sports where players frequently change their shoes, as it can be used to track exactly which athlete is wearing which pair of shoes.
By integrating RFID or Bluetooth LE into sports shoes, helmets, or jerseys, performance data such as running speed, distance, cadence, and movement patterns can be captured in real time. This data can be used to analyze the performance of the atheletes, optimize training sessions, and minimize the risk of injury.
In sports stores and sports clubs, RFID tags can be used in sports shoes for inventory tracking and RFID anti-theft protection. With the help of RFID scanners, retailers and clubs can quickly determine which shoes are in stock, which have been sold, and which are missing
By equipping sports shoes with RFID, retailers and brands are able to make personalized offers and recommendations based on customer purchase and usage data. This can help to strengthen customer loyalty and improve the shopping experience.
RFID can also be used as an authentication solution for sports shoes, to ensure that they are genuine and not counterfeit. Detailed product information such as material, manufacturing location, and care instructions can also be accessed via RFID tags.
Competitions
In competitions, RFID technology is used in various sports to identify athletes and track their performance. For example, RFID tags can be used in running shoes or race numbers to accurately record the times of runners in marathons. In team sports such as soccer, RFID tags in jerseys or balls can be used to track the position of players and collect performance data. Sensors in fitness equipment, sportswear, and wearable devices measure various parameters such as heart rate, step count, calories burned, sleep patterns, and movement.
This data is transmitted wirelessly and can be used to optimize training, monitor performance, and track health goals. The data can also be used to measure the stress levels of athletes, prevent over-training, and optimize recovery. In some sports, such as tennis and basketball, wireless IoT solutions are used to equip playing fields and courts with sensors that can track player movements and actions. This enables detailed analysis of player performance and tactics, and supports referees in their decisions.
Sports Stadiums
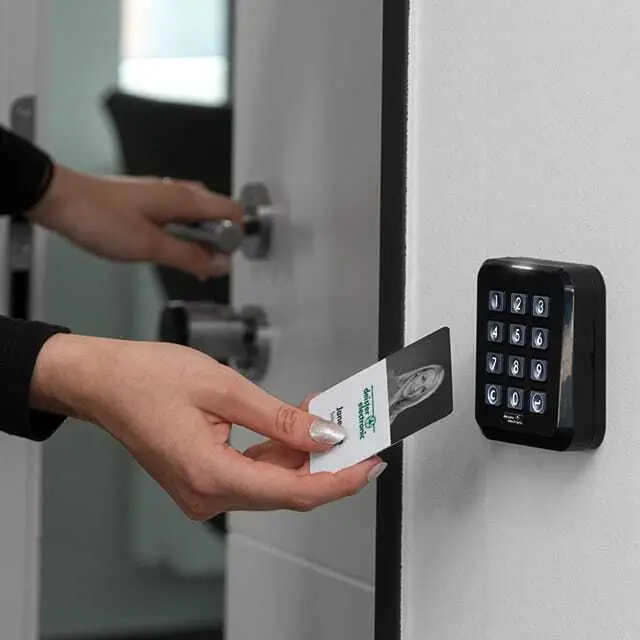
Wireless IoT technologies can also be used to improve security in sports stadiums by supporting real-time monitoring systems, intrusion detection, and access control. This enables the effective monitoring and control of access to different areas of the stadium, as well as rapid response to security incidents.
Spectators can use personalized tickets, or tickets with embedded RFID tags or NFC chips to pass through turnstiles or other access points. This enables fast and efficient ticket control and prevents queues and crowds at the entrances. Wireless payment technologies such as NFC technology and mobile wallets are used in sports stadiums for the purchase of food, drinks, merchandise items, and other services. Spectators can use their smartphones or contactless credit/debit cards to pay quickly and securely without having to carry cash.
By integrating wireless IoT solutions, tickets can also be purchased, stored, and scanned on smartphones. This offers spectators more flexibility and convenience when purchasing and accessing tickets. By integrating wireless IoT solutions, sports stadiums can also collect data on spectator behavior to provide personalized offers, promotions, and discounts. This contributes to customer loyalty and creates additional revenue opportunities for stadium operators and merchandisers. Overall, wireless IoT solutions are helping to make access to sports stadiums safer, more efficient, and more user-friendly, while creating new opportunities for customer engagement, marketing, and revenue generation.
RFID and BLE Ticketing Systems for Ski Access

Many large ski resorts, like the Dolomiti Superski in Italy that has 450 ski lifts and several hundred access points, use RFID and BLE ticketing systems for access control. Here, RFID and BLE access control systems from Axess can be used. This system involves ski passes with segmented RFID chips. Rinas Gerätetechnik provides the machines for segmenting the RFID chips. These machines apply Axess-developed data structures to divide the RFID chip into segments, enabling storage of various applications like access, ski rental, and parking on a single chip.
The ski passes with RFID chips, are personalized upon issuance. These are valid for durations ranging from one day to one week. Lift gates are fitted with long-range RFID antennas for contactless access. The card's validity is quickly verified and the gate opens. Access authorization is therefore transmitted seamlessly from the skier’s jacket or pants pocket, eliminating the need to search for the card.
Additionally, smartphones with BLE functionality enable a new access method. Tickets are stored digitally via the Axess Ski Wallet app after purchase from the online store. Upon approaching the gate's reading area, the smartphone automatically connects via Bluetooth, allowing contactless ticket verification and triggers the opening of the gate. RFID ski passes can also feature payment capabilities.
Many large ski resorts, like the Dolomiti Superski in Italy that has 450 ski lifts and several hundred access points, use RFID and BLE ticketing systems for access control. Here, RFID and BLE access control systems from Axess can be used. This system involves ski passes with segmented RFID chips. Rinas Gerätetechnik provides the machines for segmenting the RFID chips. These machines apply Axess-developed data structures to divide the RFID chip into segments, enabling storage of various applications like access, ski rental, and parking on a single chip.
The ski passes with RFID chips, are personalized upon issuance. These are valid for durations ranging from one day to one week. Lift gates are fitted with long-range RFID antennas for contactless access. The card's validity is quickly verified and the gate opens. Access authorization is therefore transmitted seamlessly from the skier’s jacket or pants pocket, eliminating the need to search for the card.
Additionally, smartphones with BLE functionality enable a new access method. Tickets are stored digitally via the Axess Ski Wallet app after purchase from the online store. Upon approaching the gate's reading area, the smartphone automatically connects via Bluetooth, allowing contactless ticket verification and triggers the opening of the gate. RFID ski passes can also feature payment capabilities.

“The company Axess has been using several segmenting machines from Rinas for the production of RFID tickets for more than 20 years. There have hardly ever been any defects on this machine, a fact that makes us very proud.”

Armin Rinas
Managing Director
Efficient Ski Pass Management with RFID

The Passo Lavazè Cross-Country Ski Center modernized its ticketing system with a cloud-based access control solution in 2022 in order to accommodate its approximately 45,000 annual visitors. The ski center has three manned entry points to its slopes. 200 meters away is the central office where wearable ski tickets or passes with integrated RFID transponders are purchased. With this RFID ski pass, skiers can track their journeys, record ski metrics, and check weather conditions on a personalized dashboard via the skier’s e-mail address.
The solution involves two gates that are equipped with CAEN RFID’s Hadron RFID modules and antennas. As skiers pass through both gates, the RFID tags on the ski passes are read, regardless of tag orientation. A ticketing software by Aroundstore.com handles the verification, validation and access authorization based on the RFID cards.
The Passo Lavazè Cross-Country Ski Center modernized its ticketing system with a cloud-based access control solution in 2022 in order to accommodate its approximately 45,000 annual visitors. The ski center has three manned entry points to its slopes. 200 meters away is the central office where wearable ski tickets or passes with integrated RFID transponders are purchased. With this RFID ski pass, skiers can track their journeys, record ski metrics, and check weather conditions on a personalized dashboard via the skier’s e-mail address.
The solution involves two gates that are equipped with CAEN RFID’s Hadron RFID modules and antennas. As skiers pass through both gates, the RFID tags on the ski passes are read, regardless of tag orientation. A ticketing software by Aroundstore.com handles the verification, validation and access authorization based on the RFID cards.

"A dual-gate RFID system ensures rapid access to the ski slopes, minimizing queue times and enhancing the overall skiing experience for visitors."

Stefano Coluccini
General Manager
Racecourse Access Control with RFID
Chester Racecourse, the oldest racecourse in the world, has been using an RFID-based mobile access control system since 2021. Around 25,000 visitors enter the racecourse per race day. Admission tickets of all visitors must be checked quickly and efficiently. The universal RFID system, developed in cooperation with HID, manages racecourse access of both staff and visitors.
RFID tickets are sent to each visitor via e-mail after purchase. Staff are issued RFID badges. The RFID badges and e-tickets are read at any one of the racecourse entrances via an RFID handheld. An event management platform oversees access authorizations, e-tickets, and event services. Employees with the RFID handhelds can verify both individual and group tickets with a single scan. The result: A much faster admission speed.
"The goal was to increase both the speed and efficiency of entry into the racecourse at all gates. Reducing the maximum number of tickets on a mobile phone app to four meant that a group of eight people could enter the premises with just two mobile phones with four tickets, as opposed to having to scan eight individual tickets. This resulted in a 60% reduction in time for ticket scanning."
Dashboard and Wi-Fi Supports Trainer Teams

The American Football League relies on the integration of RTLS (Real-Time Location Systems) from Zebra Technologies in combination with RFID tags and antennas that are optimally aligned for each stadium. UWB sensors are used for the RTLS solution. The radiation patterns are arranged as overlapping concentric circles that can capture every detail of the pitch down to individual blades of grass.
The aim is to track football players in the NFL to collect comprehensive health, movement, and fitness data. The result is detailed player statistics that support the development of training goals. Individual training should be based on the data collected, focusing on the specific needs of each player. Personalized training programs could be developed that address individual strengths and weaknesses. This could be done by analyzing movement patterns and performance data to create tailored training plans. The dashboard provides the basis for the coaches. Coaches can track player performance during training in real time on their devices via Wi-Fi and react quickly to changes and adapt training accordingly.
The American Football League relies on the integration of RTLS (Real-Time Location Systems) from Zebra Technologies in combination with RFID tags and antennas that are optimally aligned for each stadium. UWB sensors are used for the RTLS solution. The radiation patterns are arranged as overlapping concentric circles that can capture every detail of the pitch down to individual blades of grass.
The aim is to track football players in the NFL to collect comprehensive health, movement, and fitness data. The result is detailed player statistics that support the development of training goals. Individual training should be based on the data collected, focusing on the specific needs of each player. Personalized training programs could be developed that address individual strengths and weaknesses. This could be done by analyzing movement patterns and performance data to create tailored training plans. The dashboard provides the basis for the coaches. Coaches can track player performance during training in real time on their devices via Wi-Fi and react quickly to changes and adapt training accordingly.

"One of the neat features of the solution in this regard is the dashboard for coaches, who are able to see player performance at practice in real time on their devices using Wi-Fi. After an injury, teams can measure exactly how current performance compares to the previous top performance. Overall, the solution puts teams in an optimized position in terms of productivity, health, and performance on game day."

Adam Petrus