What Are Label Printers?
A label printer is a device designed to print on card stock or self-adhesive label materials. These printers are connected to a computer and uses label software to create specific labels. Label makers are label printers that have a built-in keyboard and software, and can function as a stand-alone device. Label makers do not require connection to a computer. There are three connectivity options for label printers: network, wireless or Bluetooth, and Universal Serial Bus (USB). Wireless label printers (cableless printers) use Wi-Fi or Bluetooth.
There are desktop label printers, commercial label printers, and industrial label printers.
Desktop label printers are small printers that are used in areas that have limited space, such as in retail or in offices. These printers can print up to 1,000 labels a day.
Commercial label printers are designed for businesses that require reliable and efficient label printing but do not need the heavy-duty capabilities of industrial models. These printers are suitable for medium-volume labeling tasks. These printers feature customization options like variable data printing. These options enables personalized marketing campaigns.
Industrial label printers are robust, high-performance devices designed for heavy-duty labeling tasks in demanding environments like warehouses and production plants. They are specially designed to print labels in production lines.
Industrial printers are larger in size and have higher print resolutions, compared to desktop readers. They typically feature high print speeds, large label capacities, and advanced connectivity options for integration with other industrial equipment and systems. These printers are able to print up to 10,000 labels daily, and enable industrial labeling and identification.
Label Printers and IoT
Thermal transfer label printers can be integrated with Internet of Things (IoT) to enable real-time product tracking. Internet of Things printers represent an important advancement label printing. An IoT printer communicates with sensors, databases, and cloud-based applications to automate the labeling process. The connectivity and automation provided by printers with IoT are particularly beneficial in industries like logistics and manufacturing.
NFC printers automate printing processes by allowing users to hold NFC-enabled devices close to the printers in order to trigger printing actions via a dedicated app on the device. Printers with NFC technology offer user convenience.
An RFID printer or RFID label printer is able to print and encode data on RFID labels or RFID inlays. There are three main types of RFID printers: mobile, industrial, and desktop. Industrial RFID printers can print up to 10,000 tags a day. Desktop RFID printers prints up to 500 tags daily, and a mobile RFID printer prints up to 200 tags a day. An RFID card printer prints and encodes plastic laminated cards that are used for contactless identification. The cards are equipped with an antenna and inlay that can be read by a wireless RFID reader.
What Types of Label Printers Are There?
There are four main types of label printers: Thermal Transfer (TT) and Direct Thermal (DT), Inkjet, and Laser.
Thermal transfer label printers
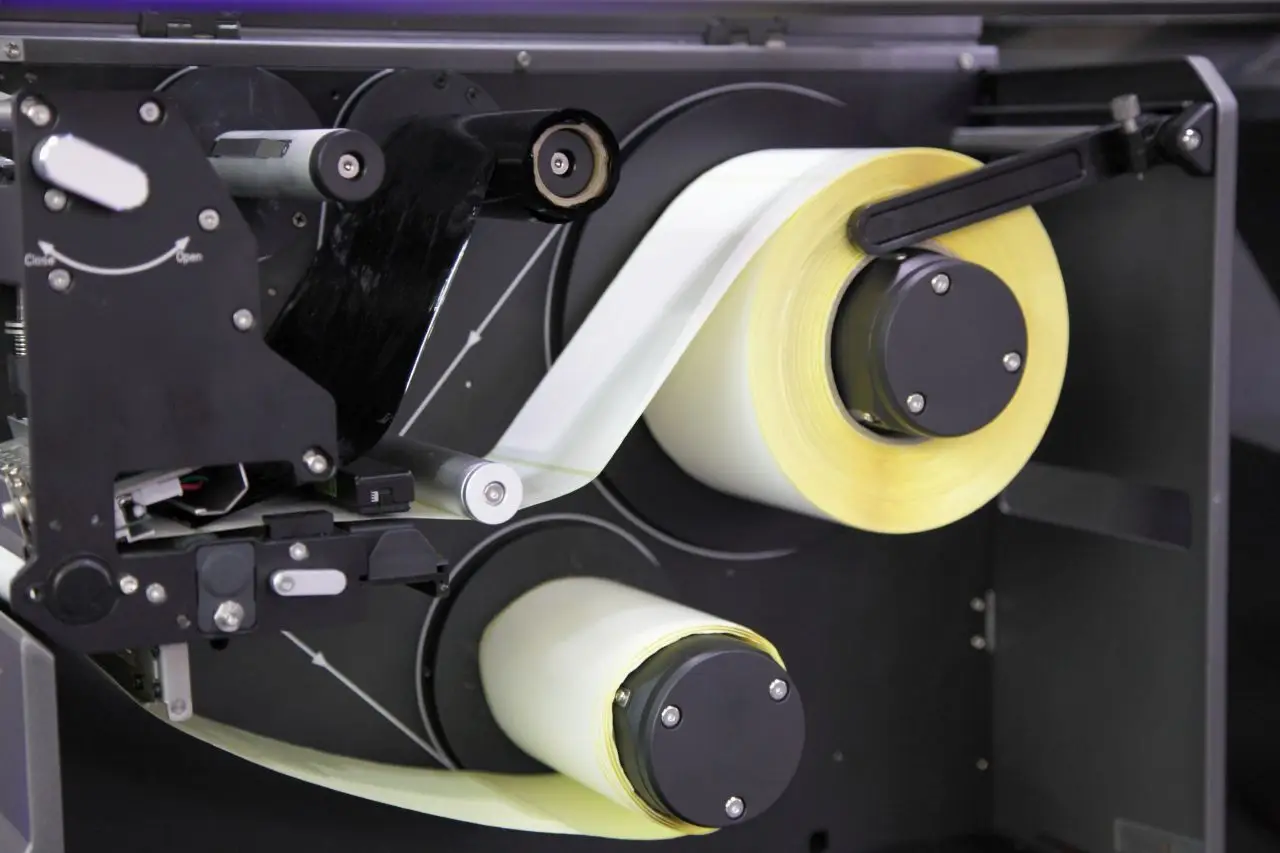
In thermal transfer label printers, heat is used to transfer ink from a carbon ribbon to the label. This creates durable and long-lasting prints. These labels are typically more robust and less sensitive to light. Thermal transfer label printers are commonly used to print outdoor labels, shelf marking labels, and barcodes, for example. They are used for applications where labels need to be used for longer periods of time, such as asset tracking. The main components of a thermal transfer printer include the thermal print head, the ribbon, resin or wax-based ink, and the label material.
Direct thermal printers
Direct thermal printers, on the other hand, do not use a ribbon. Instead, they print directly onto heat-sensitive label material that darkens when exposed to heat from the print head. No ink is required. However, the labels produced by direct thermal printers are more susceptible to environmental factors such as heat, light, and abrasion, which can cause the printed information to fade over time.
For this reason, direct thermal printing is commonly used for applications where the label's lifespan is short (less than six months), such as shipping labels, receipts, name tags, and any other temporary labeling needs. Direct thermal printers are commonly used in the food industry to print inventory labels, for example.
Label printer manufacturers have also designed label printers that are able to switch between thermal transfer and direct thermal mechanisms.
Inkjet label printers
Inkjet label printers are devices that use liquid ink to produce high-resolution images and text on labels. The ink is sprayed through tiny nozzles onto the label material (paper, cardboard, plastic, or non-woven fabrics). Customized label designs are possible. Their ability to produce full-color prints makes them a popular choice for businesses that require on-demand printing with high visual impact. They are often used to print labels for hazardous materials, for example.
Laser label printers
Laser label printers, in contrast, use laser technology to produce images and text on labels by melting toner powder onto the label material. The process involves a laser beam creating an electrostatic charge on a drum, which then attracts toner particles. The toner is then transferred to the label and fused using heat and pressure. Laser printers are well-suited for high-volume printing tasks and are known for their speed and precision. They are commonly used in office environments, industrial settings, and any application where high-quality, monochrome, or color prints are needed.