Production Systems
Production systems are fundamental to the precise manufacturing and personalization of smart cards and labels, supporting a wide range of secure and innovative applications.
- Published: May 02, 2024
- By: Anja Van Bocxlaer
- Read: 8 min
- Production systems use specialized machines for accurate manufacturing and personalization of smart cards, labels, and tickets.
- Key production stages include card body and inlay production, IC module fabrication, and personalization involving printing and chip encoding.
- Card encoders personalize cards using contact, contactless, or magnetic stripe technology to store secure data.
- RFID and NFC cards produced by these systems enable applications like access control, contactless payment, and worker safety.
- Leading manufacturers are implementing eco-friendly materials and innovative production methods to address future market requirements.
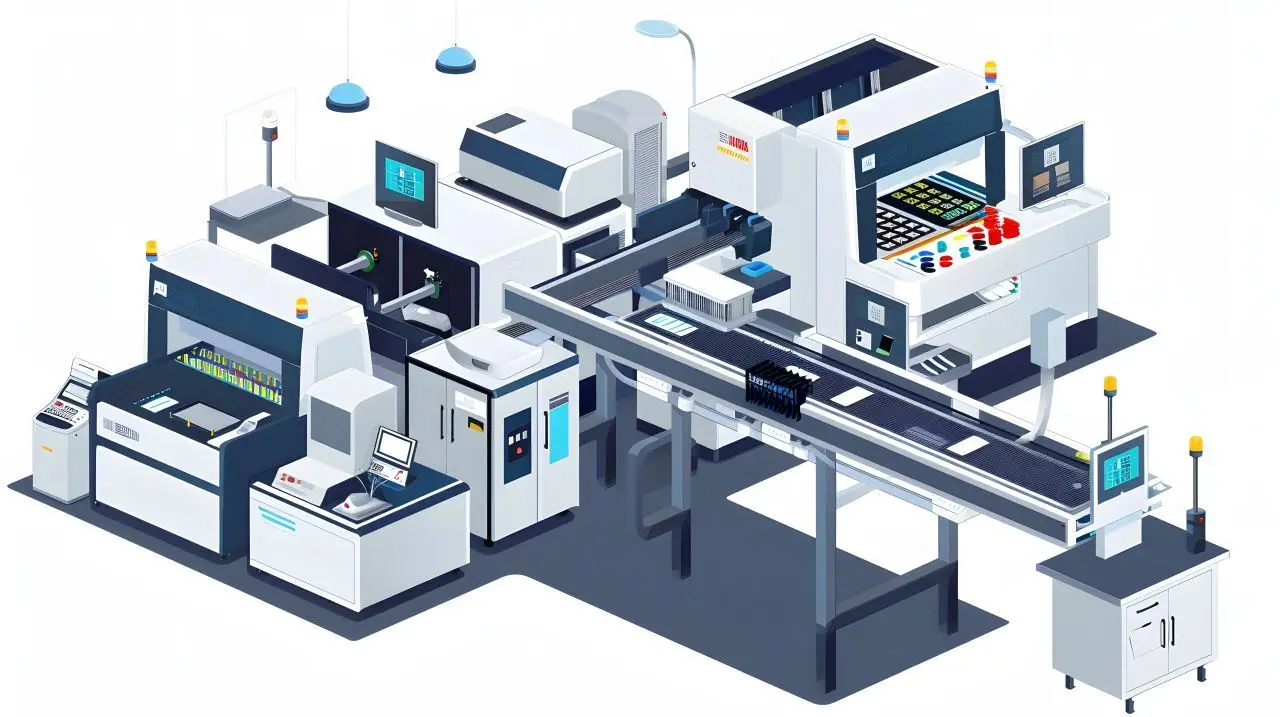

What are Production Systems?
Production systems play a central role in the manufacture of smart cards, RFID and NFC technologies. They are responsible for the precise production and personalization of smart cards, labels, tickets and barcode labels. Important features are die-cutting accuracy, precision, speed and quality, which are necessary for efficient and accurate production.
Production Systems for Labels and Tickets
Production systems for labels and tickets are specialized machines that are used to produce labels and tickets in various formats and materials.
There are different types of labels such as barcode labels and RFID labels and tickets. These labels and tickets are used for product identification and access control. RFID tickets are particularly useful for events and transportation.
Advanced printing techniques such as inkjet and thermal transfer processes are used in production facilities. These processes ensure high print quality and meet the required standards. RFID inlays and electronic chip encoding are essential for the production of RFID labels and RFID tickets. These technologies enable precise and reliable data transmission.
The production process involves several steps, from design to printing and personalization of the labels. Quality assurance is crucial to ensure that all products meet the highest standards. Regular checks and tests are part of the process.
Production Systems and Machines for Chip Cards
Chip card production facilities consist of various production machines or systems. There are many types of production machines that are specialized for the production of different kinds of chip cards, such as ID cards, payment cards, and smart cards like Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) cards, RFID cards or NFC cards. Production systems and machines work with specialized software, and follow specific standards and customer requirements.
What Processes Are Involved in Smart Card Production Systems?
Smart card production involves card body and inlay production, integrated circuit (IC) module production, and personalization. Each process uses specialized production machines and equipment that are part of a production system.
Card Body and Inlay Production
Card body and inlay production are the first stages in the manufacturing of smart cards. The card body refers to the physical structure of the card. It is typically made from materials like PVC, PET, or polycarbonate, but can also be made from wood or paper. The inlay is a component embedded within the card body that contains the antenna and the chip for contactless cards.
The processes involved in card body production are tape layering, sheet hot stamping, foil punching, inlay testing, sheet collating, sheet lamination, card punching, card inspection, card hot stamping, and quality assurance. In the inlay testing process, integrated RFID transponders in the inlays are tested to ensure that they are fully functional. In an RFID inlay production system for example, it is possible to combine all these processes in one production system or machine.
IC Module Production
IC module production is the process of creating the microchips that store and process information in smart cards. This involves the fabrication of semiconductor wafers, which are diced into individual chips. These chips are then mounted on a module for integration into the card body. The modules include contact pads for contact cards or a connection to an antenna for contactless cards. The IC modules are strictly tested to ensure they meet the requirements for security and performance.
The processes involved in IC module production include die bonding, wire bonding, encapsulation, tape inspection, molding, as well as the electrical test and pre-personalization. Each of these processes can be performed by individual production machines. These processes can can also be carried out by a single, more complex production system or machine.
Personalization
Smart card personalization is the final stage of smart card production. This stage involves precision printing, chip encoding, and chip embedding. It is an important process in card production systems. In precision printing, the cardholder's personal information, such as their name, account number, and a photograph, are printed onto the card body. High-quality printing technologies, such as thermal transfer or laser printing, are used to ensure the durability and clarity of the printed data. Batch coding machines are used in this stage.
In chip encoding, the IC chip within the card is programmed with specific data and software relevant to its intended use. This can include personal data, security keys, and payment information, for example. The encoding process is done using specialized equipment called card encoders. This will be explained in more detail in the sections below.
Chip embedding is a process necessary for the production of contactless cards. It involves embedding the encoded IC chip and the connected antenna into the card body. For contact cards, the chip is embedded in a way that its contact pads are exposed on the card surface, allowing interaction with card readers.
What Are Card Encoders?
Card encoders are devices or modules that can be added to card printing machines and production systems in order to store data into the components of cards. These devices are use to personalize cards, and are therefore also called personalization systems or machines. There are three main types of card encoders: Contact, contactless, and magnetic stripe encoders.
A card body with an integrated contact chip is placed inside a contact encoder in order for a smart contact card to be produced. Contact encoders write data like personal information and security keys to the ICs of contact smart cards. These cards have visible contact pads that interface with a reader to exchange data. Contact smart cards are cards that must be physically inserted into a reading device in order to start the reading process. Examples of contact smart cards include debit and credit cards.
Contactless encoders, on the other hand, write data to cards that use Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) or Near Field Communication (NFC) technology. These cards do not require physical contact to exchange data. Instead, they use electromagnetic fields to communicate with a reader. By placing the card over a contactless encoder, data is written onto the chip. This data includes access credentials or payment details, for example. Access control cards, contactless payment cards, and transport ticketing cards are produced using contactless encoders.
Magnetic stripe encoders are used to write data to the magnetic stripes found on the back of many cards. This data typically includes account numbers, cardholder names, for example. Magnetic stripe technology is often used for payment processing and access control, though it is being increasingly being replaced by more secure technologies like chip cards and contactless solutions. Hotel room key cards and access control cards are produced using magnetic stripe encoders.
There are encoders that are able to personalize and read different types of cards. It is possible for a specialized encoder to personalize RFID, magstripe and smart cards, for example.
Wireless IoT Technologies
RFID
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) card production systems produce RFID cards that are used for access control.
NFC
Near-Field Communication (NFC) card production systems produce NFC chip cards used for contactless payment.
QR Code
QR-Codes and barcodes are produced by production systems with labeling machines.
Applications Enabled by Chip Card Production Systems
The RFID and NFC cards produced by these production systems are used in many applications across various industries. This includes contactless payment solutions and access control, for example. By ensuring that only authorized employees can enter dangerous zones, RFID cards also contribute to worker safety. Other applications include RFID cards as part of authentication solutions in electric vehicle (EV) charging.
Example 1: RFID Production Systems by Rinas Gerätetechnik
RFID ticketing systems from the company Axess are used by ski resorts for access control. The RFID cards used for this ticketing system are produced by production machines from Rinas Gerätetechnik. The machines segment the cards so that the RFID chip enables different applications, including access, ski rental, and parking.

“The company Axess has been using several segmenting machines from Rinas for the production of RFID tickets for more than 20 years. There have hardly ever been any defects on this machine, a fact that makes us very proud.”
Armin Rinas - Managing Director, Rinas Gerätetechnik
Example 2: Chip Card Production Systems at Raiffeisendruckerei
PCI and FSC-certified card manufacturer, Raiffeisendruckerei produces plastic-free wooden payment chip cards with specially designed production systems. Production machines at Raiffeisendruckerei fold and press individual layers of wood veneer and paper. After this, card blanks are punched from a wooden sheet. A hologram is then applied via a hot stamping machine. Next, the chip is connected to the antenna and firmly implanted in a cavity on the wooden card. The last step is card personalization.

“We are currently working on mass-producing the Timbercard with the new machinery. At the same time, we are researching further Timbercard innovations with our partners in order to meet current and future customer requirements.”
Claudius Pawliczek - Division Manager/Procurator Products & Operations, Raiffeisendruckerei