Container Management: An Integral Part of the Logistics Process
Efficient container management saves costs, reduces the container volume, increases the speed of material flows, and ensures the quality of logistics processes. Shipping errors are reduced and recipients receive the goods at the agreed time. Suppliers, in turn, gain in trust. However, implementing efficient container management is not quite as simple as this list of benefits makes it sound. In order to shed light on the topic of container management in detail, it makes sense to differentiate between the terms ‘container’ and ‘load carrier’.
In most cases, containers are closed boxes, small load carriers (SLCs), crates, barrels, or drums that transport goods or merchandise. Load carriers, on the other hand, are often open carrier units that are used to hold goods. These include, for example, pallets, trolleys, mesh boxes, or containers. Load carriers often also serve as transport carriers for containers. While the system for transporting containers is referred to as container management, the control of load carriers is referred to as load carrier management. Both types of transportation are components of logistics processes in container management. The terms ‘loading equipment’ or ‘loading equipment management’ are also used.
Even more important than differentiating between the transport containers is the question of whether the containers are in an open, semi-open, or closed container circuit. In most cases, these are reusable containers that can be part of a pool system. These containers protect the goods and are often weatherproof. In order to track containers in our digital world, and to control and monitor these containers in real time, shippers, freight forwarders or expeditors use container management.
Wireless IoT Technologies and Container Management
Products Designed for Container Tracking
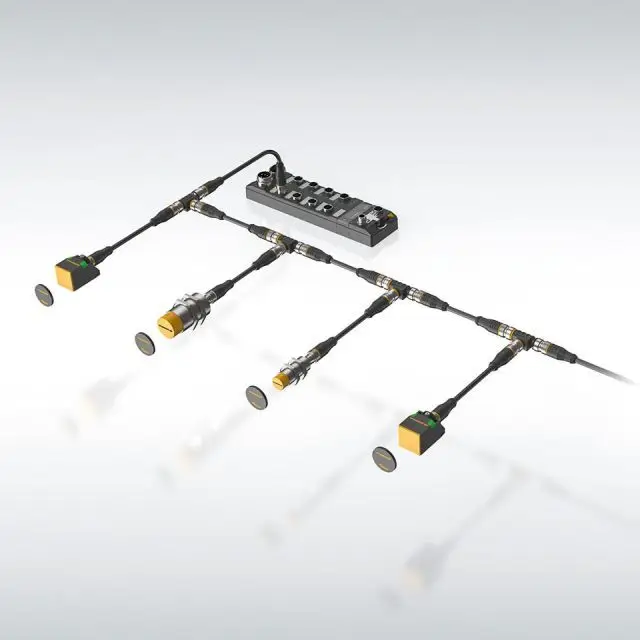
Every container identification technology is based on a data carrier in the form of transponders, labels, LPWAN or BLE sensors, and GPS trackers. These data carriers send information to IoT devices. These can be read/write devices or gateways. Data carriers are also read by scanners, handhelds, or even smartphones. In most cases, both mobile and stationary readers are used. Numerous web-based solutions with intuitive devices are available on the market.
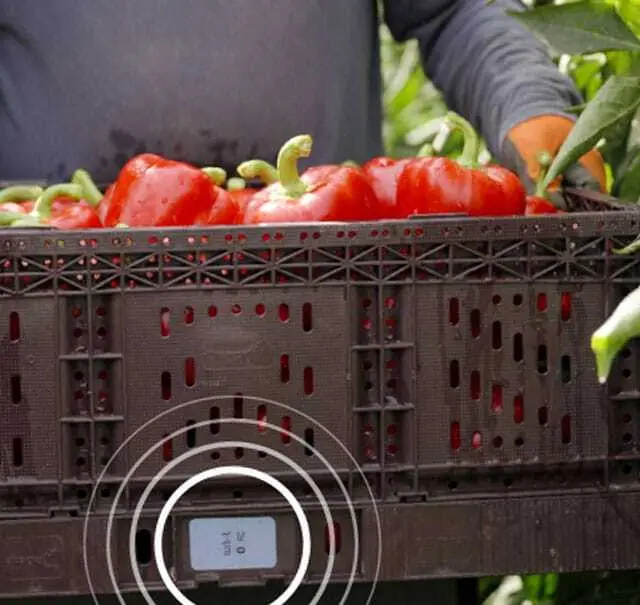
The more valuable the goods to be transported, the more security-relevant the digital identification of the container is. Sensors measure data such as temperature, humidity, acceleration, or vibrations, and send this data to IoT devices. This enables the condition monitoring of the container and the goods.
Cloud computing helps companies to monitor a very large volume of containers and to analyze the movements of these containers. By using data analysis techniques such as machine learning and AI in companies, predictive forecasts can be made about transportation risks. The transition at gates or at truck loading areas is often also equipped with industrial identification hardware to track the transportation of containers.
Facts & Figures
Containers come in all shapes and sizes and are crucial in many industries. According to a report by the data and business intelligence platform ‘Statista’, approximately 80 percent of all goods in world trade are shipped via the sea. Over a billion metric tons of cargo were globally shipped by sea in 2021. The market for shipping containers was valued at around 7 billion USD in 2021. This number is expected to grow to approximately 16 billion USD by 2028.
According to a report by the advisory firm for management strategy and market research ‘International Market Analysis Research and Consulting Group (IMARC Group)’, the global market for smart containers was valued at over 3 billion USD in 2023. This market is expected to grow to over 13 billion USD by 2032, as a result of the increasing demand for goods tracking and real-time monitoring.
Practical Examples of Container Management
The following success stories from real-world economy show which use cases are possible with wireless IoT technologies, for example in the logistics, smart city, and retail sectors. What are the benefits for companies and processes, and why did company management opt for this particular technology? The following solutions are based on real success stories.
Waste Container Management in Heidelberg

Topics such as "waste disposal" are often the subject of intense discussion in administrations. The wireless IoT technology LoRaWAN has already been tried and tested in the smart city sector. These applications are usually limited to specific areas, such as cities or industrial areas, which makes local scalable networks possible. LoRaWAN offers the wireless functionality of sensors in metal containers. This allows the fill levels of waste garbage cans, glass containers, water and salt silos to be monitored so that their collection can be controlled centrally. As waste garbage cans have no power supply, sensors have to work autonomously. LoRaWAN sensors have a service life of up to six years.
In 2021, Pepperl+Fuchs installed 800 fill level sensors in glass containers in Wuppertal on behalf of the German waste management company (AWG). They are maintenance-free. In Heidelberg, sensors have been measuring the fill level of road salt containers since the winter of 2021. As part of the "Smart Winter" project, the city recorded meteorological data and supplements this with the measurement data from the road salt silos in order to optimize winter service management.
Topics such as "waste disposal" are often the subject of intense discussion in administrations. The wireless IoT technology LoRaWAN has already been tried and tested in the smart city sector. These applications are usually limited to specific areas, such as cities or industrial areas, which makes local scalable networks possible. LoRaWAN offers the wireless functionality of sensors in metal containers. This allows the fill levels of waste garbage cans, glass containers, water and salt silos to be monitored so that their collection can be controlled centrally. As waste garbage cans have no power supply, sensors have to work autonomously. LoRaWAN sensors have a service life of up to six years.
In 2021, Pepperl+Fuchs installed 800 fill level sensors in glass containers in Wuppertal on behalf of the German waste management company (AWG). They are maintenance-free. In Heidelberg, sensors have been measuring the fill level of road salt containers since the winter of 2021. As part of the "Smart Winter" project, the city recorded meteorological data and supplements this with the measurement data from the road salt silos in order to optimize winter service management.

"Due to the excellent property penetration, smart city applications are typical areas of application for LoRaWAN technology, such as recording meter readings and container fill levels. In the industrial environment, LoRaWAN can also be used for condition monitoring of machines and predictive maintenance."
Wolfgang Weber
Independent
Sustainable Cosmetic Bottles at Edeka
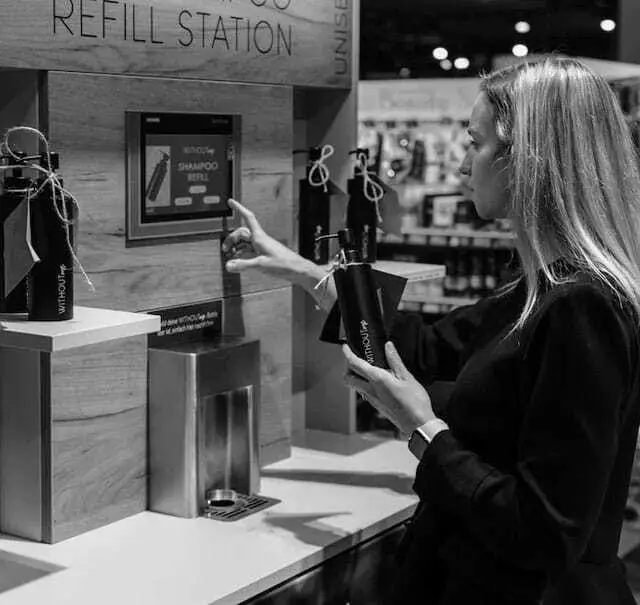

A solution based on an RFID pooling system and an automatic filling machine is being used by the start-up Withoutme for the refilling of cosmetic bottles. Stainless steel bottles are equipped with an HF RFID tag. These bottles can be used up to 100 times. In retail stores, customers can place the cosmetic bottles on the filling machine. A wireless RFID reader from Feig Electronic, positioned in the filling machine, reads the tag. After reading the tag, automatic filling is activated. At the end of the filling process, a receipt is printed, which can be paid at the checkout counter. The first filling machine was put into operation in an Edeka market in Saarbrücken in 2022.
A solution based on an RFID pooling system and an automatic filling machine is being used by the start-up Withoutme for the refilling of cosmetic bottles. Stainless steel bottles are equipped with an HF RFID tag. These bottles can be used up to 100 times. In retail stores, customers can place the cosmetic bottles on the filling machine. A wireless RFID reader from Feig Electronic, positioned in the filling machine, reads the tag. After reading the tag, automatic filling is activated. At the end of the filling process, a receipt is printed, which can be paid at the checkout counter. The first filling machine was put into operation in an Edeka market in Saarbrücken in 2022.

“RFID technology is essential for this pool solution. Without the capture of an RFID tag by the reader, the bottles will not be refilled. The unique identification of each bottle also provides insight into consumer purchasing behavior. The system records which bottle is refilled with which product and how often. In the future, the refill station could handle between 30 and 40 products.”
Steffanie Rainer
CEO
RTI Management at Recalo

The constant tracking of returnable transport items (RTIs) is crucial for efficient shipping logistics. The logistics service provider Recalo from Laatzen near Hanover in Germany offers its customers an RTI pool of 90,000 units. The company uses an RFID track and trace solution from Turck Vilant Systems to track these containers and thus ensure constant availability. Advantages of the RFID system: high data quality, fast mass recording, real-time localization and process automation.
Why UHF RFID? Bulk registration of items with barcodes is not efficient enough for this logistics company. Employees use forklift trucks to transport stacks of boxes through an RFID gate that captures identification numbers. The aim of the integration was to improve the quality of logistics processes and reduce costs.
The constant tracking of returnable transport items (RTIs) is crucial for efficient shipping logistics. The logistics service provider Recalo from Laatzen near Hanover in Germany offers its customers an RTI pool of 90,000 units. The company uses an RFID track and trace solution from Turck Vilant Systems to track these containers and thus ensure constant availability. Advantages of the RFID system: high data quality, fast mass recording, real-time localization and process automation.
Why UHF RFID? Bulk registration of items with barcodes is not efficient enough for this logistics company. Employees use forklift trucks to transport stacks of boxes through an RFID gate that captures identification numbers. The aim of the integration was to improve the quality of logistics processes and reduce costs.

"It is essential for us to know where our returnable load carriers are at any given time. This means that we will also gradually equip our foreign locations with RFID technology so that we have the greatest possible transparency in the flow of goods."

Daniel Van der Vorst
CIO
More Stories on Container Management
How is Wireless IoT Changing Modern Container Management?
Container management is a form of supply chain asset tracking. IoT and container management generates added value, as labeled containers can communicate automatically and without contact with gates or other IoT devices. With the help of IT-supported container management, complex container movements can be visualized along the entire supply chain. The data collected on the status, location, and movement of the containers can be evaluated and processed centrally. This ensures that the goods to be transported reach their destination as planned.
IoT also enables companies to monitor and control a large volume of containers, like an entire fleet of containers, for example. Based on the movement data, decisions can be made regarding the optimization of logistics processes. Real-time container monitoring increases the quality of the entire transport process. This benefits the entire digitalized supply chain. It is also possible to predict possible future risks using AI and data analysis.
Modern Container Management for Companies
Container management with RFID is a modern solution to the challenges of warehouse management. By using RFID containers and specialized software, companies can monitor their inventory in real time, improve the accuracy of inventory data and reduce costs. The introduction of such systems offers significant long-term benefits in terms of efficiency and profitability.
The implementation of RFID-based container management systems requires careful selection of RFID hardware and the integration of powerful inventory management software. Staff training and regular maintenance and monitoring of the system are also crucial to ensure maximum efficiency and accuracy.
Container Management Reduces the Carbon Footprint
Advantages of Wireless IoT
- Large container volumes
- Real-time localization
- Pool solutions
- Reduced carbon footprint
- Cost reduction
The larger the container volume and the higher the quality of the goods to be transported, the greater the benefits of introducing efficient container management based on labeled containers. By using sensor technology, the condition of the container and therefore also of the goods to be transported can be monitored. This applies in particular to vibrations and weather influences. Temperature monitoring is also made possible.
The transmission of real-time data also allows conclusions to be drawn as to whether transportation is possible within the specified time window. The movement of the containers can be tracked transparently. If there is a deviation in the delivery date, customers can be informed at an early stage.
The use of AI also makes it possible to increase efficiency and to reduce costs. Empty runs are avoided and the number of incorrect deliveries is reduced. These two factors contribute to sustainability for companies, as they reduce the CO2 footprint. Another advantage is the monitoring of container conditions. The containers have to go through container cleaning systems on a regular basis. These cleaning cycles can be monitored and, if necessary, documented.
The larger the container volume and the higher the quality of the goods to be transported, the greater the benefits of introducing efficient container management based on labeled containers. By using sensor technology, the condition of the container and therefore also of the goods to be transported can be monitored. This applies in particular to vibrations and weather influences. Temperature monitoring is also made possible.
The transmission of real-time data also allows conclusions to be drawn as to whether transportation is possible within the specified time window. The movement of the containers can be tracked transparently. If there is a deviation in the delivery date, customers can be informed at an early stage.
The use of AI also makes it possible to increase efficiency and to reduce costs. Empty runs are avoided and the number of incorrect deliveries is reduced. These two factors contribute to sustainability for companies, as they reduce the CO2 footprint. Another advantage is the monitoring of container conditions. The containers have to go through container cleaning systems on a regular basis. These cleaning cycles can be monitored and, if necessary, documented.
Advantages of Wireless IoT
- Large container volumes
- Real-time localization
- Pool solutions
- Reduced carbon footprint
- Cost reduction
Challenges: Hygiene and Security of Containers
For companies that have not yet integrated container management into their logistics processes, it is advisable to work with experts to determine the challenges for the introduction of container management. It is important to precisely define the goals and optimization for the transport processes and to analyze the transport containers in detail right from the start.
How large is the container pool? Should only an internal or also an external container cycle be mapped? Are all containers uniform? Are the containers already standardized? Should interoperability be established between different players in the supply chain? Does it make sense to introduce a pool system or return system? How many customers are supplied? Numerous questions are linked to the introduction of a new system. These include deciding on an identification technology and the associated hardware and software. In most cases, the driving force behind the implementation of container management is mainly the lack of transparency about the location, amount, and the condition of the containers. However, container management could also simply reduce the number of trips or inefficient use. This requirement will represent additional complexity, but is certainly achievable. Regulatory requirements and compliance could also be a challenge. This applies in particular to the food and pharmaceutical industries. These industries have strict requirements for traceability, hygiene, and container security. However, the benefits of container management can also be seen in terms of container hygiene. The cleaning cycles can be documented for each individual container.