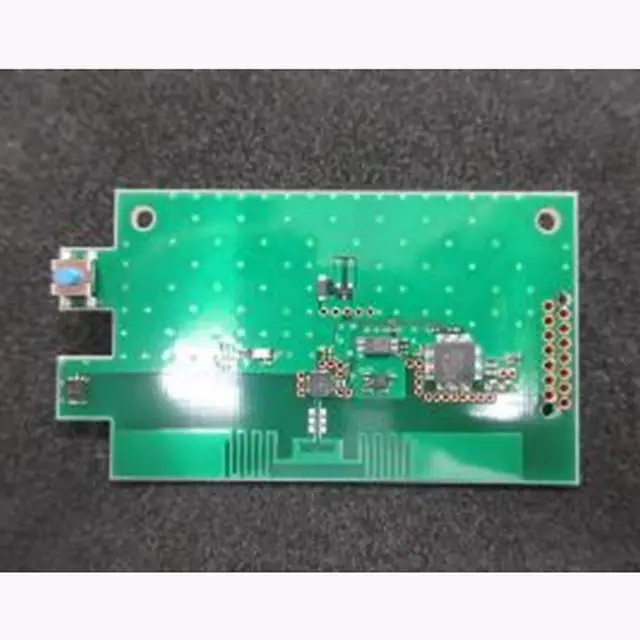
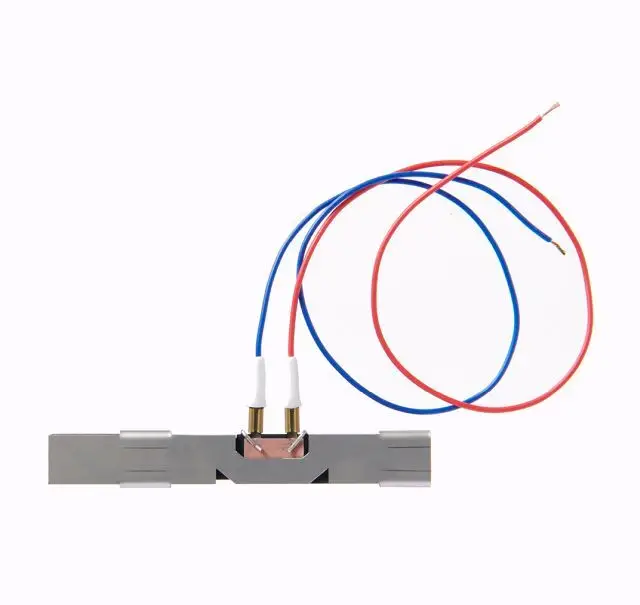
What are Smart Sensors?
Smart sensors, also known as intelligent sensors, are autonomous devices that go beyond the basic function of detecting and measuring physical phenomena like temperature, pressure, motion, or light. Traditional sensors turn into smart sensors with the integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) and computing technologies.
Unlike with traditional sensors, sensor manufacturers integrate multiple components in smart sensors that not only capture, but also process and wirelessly communicate data. In other words, sensor chips capture physical phenomena and convert them into electronic signals by incorporating semiconductor sensor circuits. This data is then used to enable various applications across various industries. The data captured by sensor chips can be used to create digital twins in industrial environments, for example. Further examples of smart sensor applications are explained in the sections below.
When it comes to Internet of Things sensors, various technologies play a key role in enabling the networking and automation of systems. RFID sensors are particularly important here, as they offer an efficient and reliable method of identifying and tracking objects. With RFID sensor technology and RFID sensor transponders, it is possible to transmit and receive data wirelessly.
NFC sensor transponders are particularly suitable for secure and fast data transmission thanks to their short-range communication. This technology is often used in applications such as contactless payment or access control. Surface Acoustic Wave (SAW) sensors are also used, which can measure physical parameters such as temperature and pressure without the need for an external power supply.
In a smart sensor network, individual sensors are added as sensor nodes. Sensor networks can either be wired, wireless, or a combination of both. An intelligent sensor network typically consists of the following components: smart sensor nodes, a sensor control module (SCM), base control modules (BCM), embedded processing, a power management control module, multi sensor data fusion (MSDF), and application software. 5G is increasingly being used as a communication technology for smart sensor networks.
What Types of Smart Sensors Are There?
There are seven main types of smart sensors. Each of these sensor types can be integrated with different IoT technologies, including RFID, NFC, UWB, LPWAN, and BLE, for example.
Acoustic Sensors
Acoustic sensors detect sound waves, as well as audio vibrations and frequencies in the environment. These smart sensors are used to determine location, intensity, and activity.
Chemical Sensors
Chemical sensors detect and respond to chemical substances in the environment. They measure the concentration of chemical and biological compounds, in addition to fluid composition.
Electrical Sensors
Electrical sensors measure electrical quantities such as voltage, current, and power. These sensors are used to detect disruptions or changes in magnetic or electrical signals on the basis of environmental conditions.
Environmental Sensors
Environmental sensors monitor various environmental parameters such as temperature, moisture, light, airflow, humidity, and pressure.
Image Sensors
Image sensors capture light waves and convert them into electrical signals. They provide an optical form that is used for visible condition monitoring. The most common types are complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) sensors and charge coupled device (CCD) sensors.
Motion and Force Sensors
Motion sensors detect movement while force sensors measure applied force or pressure. Proximity sensors are an example of smart motion sensors. Smart force sensors are typically used for weighing heavy goods in industrial environments. Strain gage sensors convert force, tension, weight, and pressure into electrical resistance.
Touch Sensors
Touch sensors detect physical touch or pressure on a surface. These sensors are often used in robotics.
What Are Smart Sensors Made Of?
There are five key components of a smart sensor: A microprocessor unit (MPU), energy harvesting capabilities or a battery, a transceiver, a memory unit, and a communication module. All functions of the smart sensor are managed by the microprocessor, which performs two functions: Signal conditioning and self-diagnosis. MPUs should be designed to operate on low power consumption to enable a long lifespan and prevent frequent battery replacements.
Smart sensors can either be battery-powered or self-powered. Self-powered smart sensors source or scavenge the energy required to function autonomously from the surrounding environment. This process is called energy harvesting. Energy sources include light, vibration, or heat, for example. The transceiver is the component that interacts with the surrounding environment and collects physical, biological, or chemical data. The memory unit either stores, or processes the collected data using algorithms.
The communication module or interface enables the connection between smart sensors and the Internet or a private cloud computing environment. This allows smart sensors to communicate with external devices. Communication can either be wired or wireless. Communication protocols govern smart sensor communication. Zigbee, LoRaWAN, Bluetooth LE, and Wi-Fi are examples of communication protocols that are commonly used in smart sensors.
Wireless IoT Technologies
Sensor-Based Products
Applications For Smart Sensors
Smart acoustic sensors can be used in various industries. In healthcare, they are typically used for patient monitoring. Speech, sleep disorders, coughing, or breathing can be monitored, for example. In industry, smart acoustic sensors are used for condition monitoring and also enable an automated quality control. These sensors can be used to detect pneumatic actuator leakage, for example.
In the security sector, smart acoustic sensors are used in combination with microphone arrays for noise reduction. The goal is the separation of specific sounds in order to locate and monitor sources of sound. Possible applications include detecting and locating unauthorized drones, and preventing vandalism and burglaries by detecting the sound of spray cans or broken glass.
As part of digitalization in the automotive industry, smart acoustic sensors enable the car to “hear”. In “The Hearing Car” project of Fraunhofer Institute for Digital Media Technology (IDMT), smart acoustics sensors and AI algorithms are used to detect and recognize sounds like sirens.
Chemical sensors are often used for environmental monitoring. Air and water pollution can be monitored through the detection of hazardous substances. As part of digitalization in industry, smart chemical sensors are used to detect leakage or spillage by monitoring chemical reactions. The use of smart chemical sensors to analyze biological samples contributes to digitalization in healthcare. In food retail, these sensors are used to ensure food safety. Allergens, contaminants, and spoilage can be detected in food products. Security applications include the identification of explosives or chemical warfare agents.
Electrical sensors are used for power monitoring in smart homes, ensuring the stability and efficiency of electrical grids, and are commonly used in consumer electronics to manage battery performance and energy consumption.
Environmental sensors are often used as part of digitalization in agriculture and as part of a smart city (digital city). In agriculture, smart moisture sensors measure soil moisture levels in order to optimize irrigation, for example. In smart cities, environmental sensors are used to monitor air quality by detecting dust levels in outdoor areas. Smart gas sensors are also used for air quality monitoring in facilities and smart homes. As another example, humidity sensors are used to measure humidity in industrial settings and greenhouses. They can even be used meteorology stations to help predict weather conditions.
Temperature monitoring is also a big area of application for smart environmental sensors. These sensors are used in industrial environments to monitor the temperature of machinery. In the smart home, smart thermostats use these sensors to measure and monitor indoor temperatures. Smart pressure sensors can be used to enable indoor navigation, stabilize drone altitudes, and optimize the calorie counting function in wearables. They measure atmospheric or fluid pressure, and are used in weather stations, automotive systems, and industrial automation.
CMOS sensors are widely used in digital cameras and smartphones due to their efficiency and lower cost. CCD sensors are found in high-end cameras and scientific imaging equipment, providing superior image quality.
Smart image sensors are used as part of vision systems that are often connected to computers with artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms. The result: Smart machine vision. Cameras with smart image sensors are used for remote monitoring and surveillance, precision agriculture, and traffic monitoring.
Smart motion sensors are often used in security-based access control applications. They are used in smart homes, or in facilities to detect motion to prevent or alert in case of unauthorized access. These sensors are also used in smart buildings to detect the occupancy of rooms. This way, lighting can be automatically switched off in rooms where no motion is detected. This promotes sustainability for companies, for example.
Proximity sensors detect the presence of other objects to prevent collisions. These sensors can be used in facilities like warehouse to prevent forklift collisions, or in events where social distancing should be enforced.
Smart force sensors are used in luggage scales in airports, or in the healthcare industry where they are used for fluid monitoring, in MRI machines, and other medical equipment. These sensors are also used in the automotive and aerospace industries. Strain gage sensors are used to monitor industrial equipment, and are also used in scientific experiments.
Robots with touch sensors can perform basic movements and detect touch. These sensors are also used in smartphones, as well as in industrial and automotive applications. In smart homes, faucets with touch sensors are used to control running water.
Example 1: Temperature Monitoring Sensors in Use at Shufersal
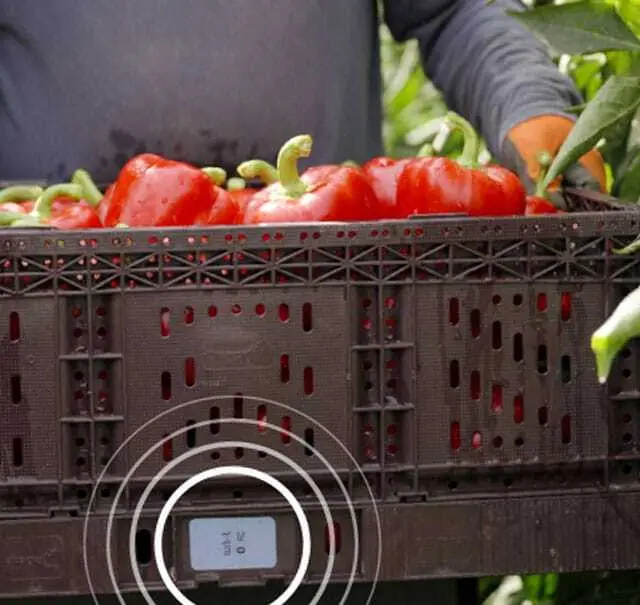

Israeli supermarket chain Shufersal uses battery-free Bluetooth IoT pixels from Wiliot to monitor the temperature of vegetable crates throughout the supply chain. These pixels are equipped with a temperature sensor. The goal is to maintain product quality and freshness. Temperature data of the vegetables is transmitted from the harvest field to the end consumer through the IoT pixels. One million Returnable Transport Items (RTIs) were equipped with IoT pixels by the end of 2023.
Israeli supermarket chain Shufersal uses battery-free Bluetooth IoT pixels from Wiliot to monitor the temperature of vegetable crates throughout the supply chain. These pixels are equipped with a temperature sensor. The goal is to maintain product quality and freshness. Temperature data of the vegetables is transmitted from the harvest field to the end consumer through the IoT pixels. One million Returnable Transport Items (RTIs) were equipped with IoT pixels by the end of 2023.

Example 2: UWB Radar Sensors for Localization and Monitoring
A UWB radar sensor solution has been deployed for the monitoring of elderly people in their homes. Developed as part of a collaborative research project of the UK Dementia Research Institute, the Imperial College London, and the University of Oslo (UiO), the solution enables the positioning and tracking of people 24/7 within the house. The UWB sensor radars are able to capture differences in gait patterns between individuals. Gait features are the key to assess drug efficacy, predicting the likelihood of falls, and quantifying fragility. An alarm is triggered when deviations from normal behavior is detected.